Sea buckthorn, planting, growing and harvesting
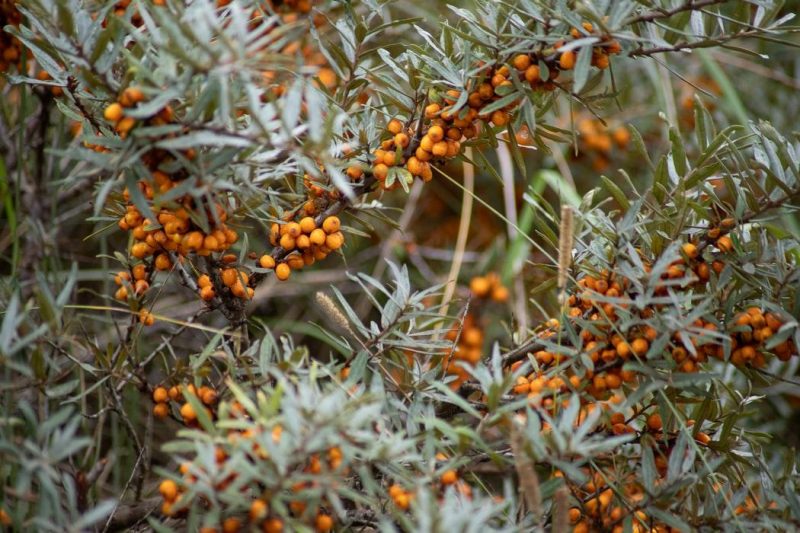

Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) is a rustic species, frequently found in hilly and mountainous areas. It is a species with a very high ecological plasticity, growing and developing on salty, acidic, or sandy soils. It can improve eroded soils and it can fix slopes. Sea buckthorn is resistant to frost, drought, and wind. Sea buckthorn fruits contain large amounts of vitamins and nutrients (C, A, B, K, iron, calcium, sodium, and magnesium), used in the pharmaceutical and food industry.
Botanical characteristics
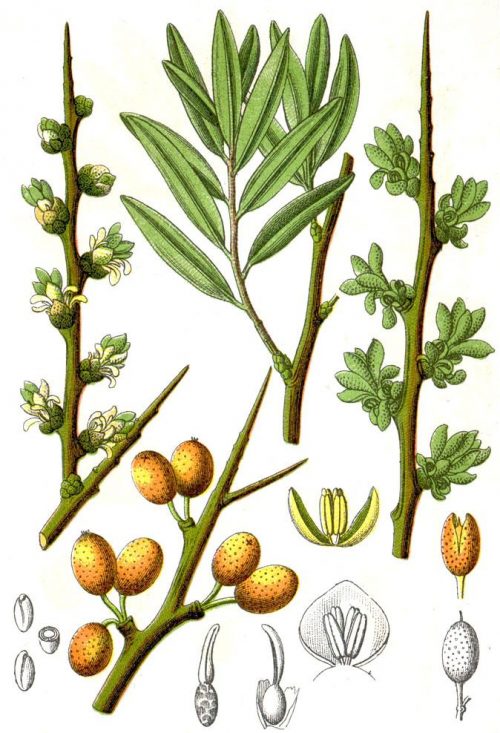
Sea buckthorn is a fruit-bearing shrub that grows as a bush, between 1.5 and 5 m tall. It grows as a creeping bush in harsh climates (high altitudes or arid areas).
The male plants are more vigorous, have longer annual growths, are darker in color and the buds are visibly more developed. The male flowers form on the annual branches and are organized in brown formations called cones. They bloom earlier than the female flowers. Female plants flower as soon as the leaves appear, and the flowers are grouped in raceme-like inflorescences. The flowering period is between March and April. Pollination is carried out by wind, which is why the ratio of male to female plants in the plantation is 1:8.
The stem has numerous sharp and very resistant thorns. The leaves are small, silvery, linear-lanceolate, and alternately arranged. The root system is well developed, both vertically and horizontally, and has a draining capacity.
The fruit is a fleshy orange berry. The fruit ripens from the first part of August to the end of October. At the peak of production, the fruit yield reaches about 25 tonnes/ha. After 18 to 20 years, the plantation goes into decline and yields drop significantly.
Environmental requirements
This species has high light requirements, and in shady conditions, the crown becomes thinner. Sea buckthorn is not a temperature-demanding species. It tolerates winter frost well, withstanding temperatures down to -40℃, and is unaffected by summer heatwaves, withstanding temperatures up to 45℃. It takes good advantage of all soil types, including eroded, sandy, and stony soils, but does not tolerate soils with excess moisture.
Soil preparation
Although it has a high ecological plasticity, high yields are obtained on flat, highly permeable, fertile, south-facing soils. The soil should not have excess moisture and a pH below 5.5. Good results can be obtained on alluvial soils, near rivers, with groundwater depths above 1.5 m.
After removing the preceding crop residues from the soil, you can scarify the soil to a depth of 50-60 cm. In autumn, plow the soil 25-35 cm deep.
Planting
The best time to plant is in autumn, during October. If planting is not possible in autumn, it can also be done in early spring. Planting distances are chosen according to the crop technology. Thus, the distances between rows and between plants per row can be as follows:
- 3 m x 2 m – in the case of a flattened crown;
- 4 m x 2,5 m – in the case of the globular crown;
- 4 m x 1,5 m – in the case of super-intensive plantations.
After establishing the planting scheme, the plot must be picketed, which consists of marking the position of each plant on the plot. This operation must take into account the 1:8 ratio of male to female plants. This means that 12% of the plants must be male. The rows should be orientated north-south as much as possible so that the plants benefit from light throughout the day. The rows should also be positioned in the direction of a permanent wind, to ensure that pollen spreads.
Planting
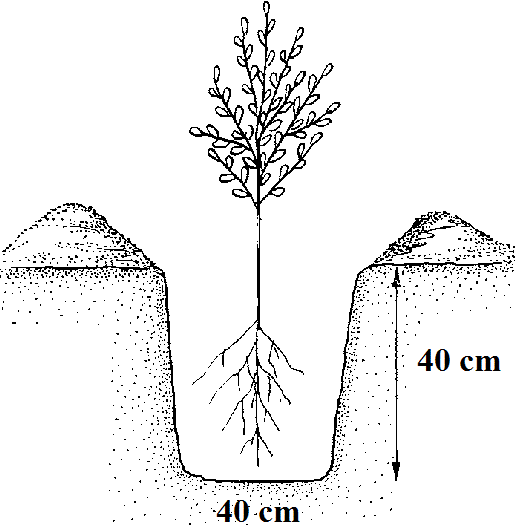
The next steps are the digging the pits and the actual planting. The holes must be 40x40x40 cm and can be made by hand or with a drill. Before planting, the planting material should be trimmed, removing dry or damaged roots. Shorten healthy roots to 20-22 cm. For a successful planting, the plants should be introduced with the roots in a sour cream consistency mud, formed of yellow earth, cattle manure, and water.
Planting should be done in such a way that the roots are placed in the hole and the plant is upright. The soil must be compacted around the plant to ensure the best possible contact between the roots and the soil. The plants must be watered immediately after planting.
Maintenance work
During the first two years after planting, you should pay special attention to the soil maintenance. Young sea buckthorn plants are sensitive to weeds, and the presence of weeds affects their growth and development. The ground should be kept clean by repeated manual or mechanized hoeing. If the work is done mechanically, a disc, a harrow, or a ground cutter can be used. The soil should be mobilized to a depth of 8-10 cm so as not to destroy the roots of the shrubs. The use of herbicides in the first years is not recommended, because sea buckthorn plants are sensitive to these substances. In areas where there is a danger of rodent attack, the stem should be protected with paper strips, nets, etc.
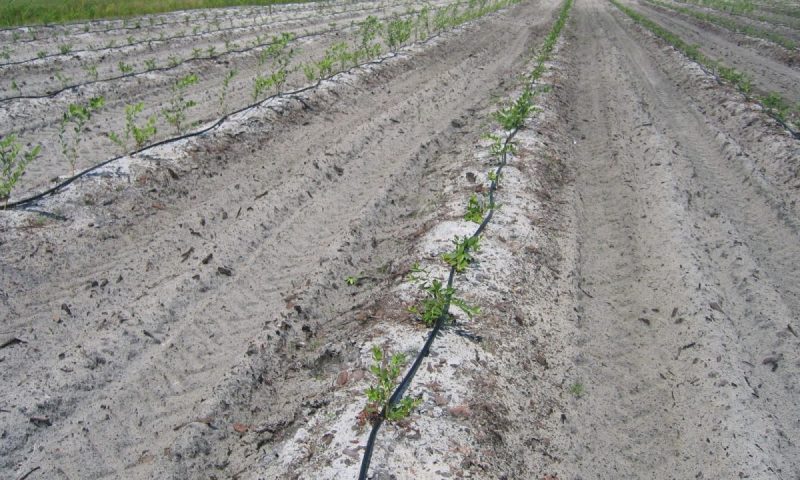
Irrigation
An important work that ensures high and constant yields is irrigation. In the first two years, the extra water supply ensures plant establishment, growth, and crown formation. Watering rates depend on soil properties and climatic conditions. They range from 300 to 400 cubic meters per hectare. It is recommended to irrigate by sprinkler or by dripping.
Pruning
Pruning is an important work in sea buckthorn cultivation technology, which aims to form the crown, promote fruit production, and facilitate maintenance and harvesting activities. Sea buckthorn tolerates well the pruning interventions and can be grown in various forms. In commercial plantations, the most common forms are the globular crown and the flattened crown. Pruning should be carried out annually, as the fruit forms towards the outside of the crown, and the plants quickly wither. Pruning should be carried out when the fruit is harvested and, if necessary, during the dormant period.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
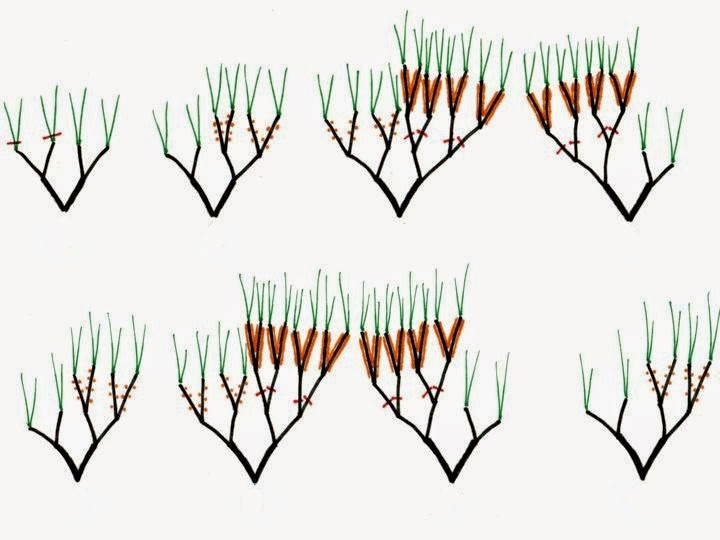
How to obtain a globular crown?
Immediately after planting, choose the central axis and shorten it to one-third of its length. In the second and third years, follow the formation of the main branches. These should be inserted on the central axis at a distance of about 30 cm from each other, arranged alternately. In the following years, complete the crown formation and start the fructification pruning. The simplest method is to prune the vegetative and fruiting growths on one side of the crown, and in the following year to prune on the opposite side of the crown. In this way each year the crown will rejuvenate and produce fruit.
How to obtain a flattened crown?
After planting, choose a main stem and two branches positioned in the direction of the rows. Shorten the central axis to 30-40 cm tall. The axis and the two branches form the first layer of the crown. In the following years, choose two more shoots, 25-30 cm away from the first layer, and form the next layers of the crown.
Fertilization
After 2 years, the roots of sea buckthorn plants start to capture nitrogen from the atmosphere and make it available to the plants. From the third year onwards, the plantation needs additional fertilization to reach its production potential. Depending on the phenotype, you can apply macro- and micro-nutrient fertilizers in the necessary quantities.
Root fertilization can be complemented with foliar fertilizers, depending on the plant’s needs and the environmental conditions. To help plants overcome periods of stress, you can apply specific foliar and root fertilizers.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Pest control
Among the main diseases encountered in sea buckthorn plantations, we mention: verticillium wilt, fusarium wilt, and rust. As pests, aphids, cicadas, and mites are the most frequent ones.
Sea buckthorn harvesting
Harvesting is one of the most difficult tasks in a sea buckthorn plantation. The fruits are arranged closely around the branches, wrapping them like a sleeve. The fruit is tightly attached to the branches and can be damaged during harvest. On the other hand, this strong grip on the branches makes it possible to prolong harvesting even into early spring. The optimum harvest time is determined by the crop destination and harvesting method.
The best period for harvesting is from the end of summer to the end of autumn. Harvesting can be done manually, mechanized, or by cutting branches. Manual harvesting is done by workers and has a low efficiency. Mechanized harvesting is the most efficient and is done with a device that shakes the Sea buckthorn bushes, and the fruits fall on polyethylene foils placed on the ground. Besides these two methods, harvesting can be done by cutting the branches. The fruit-laden branches are cut off and transported to specially designed areas, where the fruit detaches from the branches. This method is moderately efficient but, if not carried out correctly, can have a negative influence on the following years’ yields.