Radishes, treatments against pests and disease

Radish (Raphanus sativus) is a species grown mainly in temperate areas for its tuberous, succulent roots. It is a very popular species in Europe. The most widely cultivated types of radish are white summer radish and black winter radish. The radishes can be affected by pests and diseases, against which it’s important to apply the right treatments.
The main diseases of radishes
Viruses
Cauliflower mosaic virus
The leaves of attacked plants show discolored veins, yellowed interveinal tissues, and symptoms of transparency. Leaves have a deformed appearance, with twisted edges towards the upper face. Affected shoots remain small and mature plants have low yields. This disease can occur in all plants of the Brassicaceae family. Chlorotic (discolored) rings may appear on the leaves. The virus is transmitted from one year to the next through infected seeds. During the growing season, it is transmitted by insects.
Prevention and control measures:
- using healthy and certified seeds;
- removing and destroying plants showing symptoms;
- carrying out specific insecticides to control the insect population.
Bacteriosis
Bacterial leaf spot (Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola)
The infection shows up as small, dark, moist spots on both sides of the leaves. These spots can spread if conditions are favorable. The leaf margins may turn purple. Severe infections can lead to premature leaf drop.
Prevention and control measures:
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- using healthy seeds or seedlings;
- treatments with approved fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Downy mildew (Peronospora brassicae)
The disease shows yellow, irregular spots on the leaves, which later turn brown. On the lower part of the leaves appears a greyish fuzz. During the growing season, the disease spreads very easily by wind, and high atmospheric humidity conditions favor rapid expansion. The fungus also attacks the underground organs of the plant. On the roots, the symptoms appear as large, circular, black spots.
Prevention and control measures:
- using resistant varieties;
- removing attacked plants from the crop;
- specific radish treatments with fungicide, during the growing season.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
White rust (Albugo candida)
The disease is manifested by the appearance of yellowish spots on the leaves. On the underside of the leaves, opposite the spots, the fungus fructifications appear. Severely infected leaves dry out and fall off. On the stem, the attack is characterized by a deformed growth.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvesting;
- using healthy seeds;
- radishes treatments with approved fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum)
Initial symptoms show lower leaf wilting. Often the fungus obstructs the vessels on one side of the plant. The attacked leaves turn brown and fall off, and then the whole plant wilts.
Prevention and control measures:
- using healthy, certified seed;
- removing affected plants from the crop;
- radishes treatments during the growing season with specific fungicides.
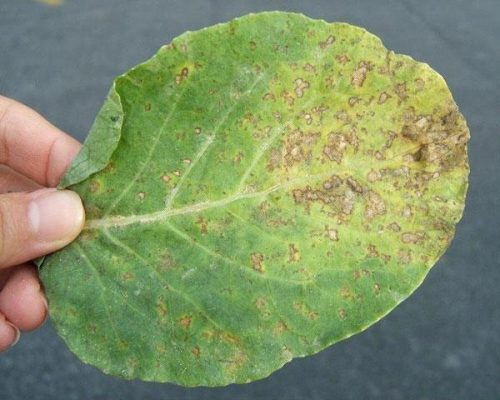
Alternaria black spot (Alternaria brassicae)
Circular brown spots appear on the leaves. The spots enlarge gradually and become surrounded by a yellow edge after which the tissue dries and falls off. Similar spots may appear on the leaf petiole. The disease encourages fungal or bacterial rots.
Prevention and control measures:
- correct crop rotation (radish crop can return to the same land after 1-2 years);
- disinfecting seeds and substrate for seedlings;
- removing affected plants from the crop;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- specific fungicide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
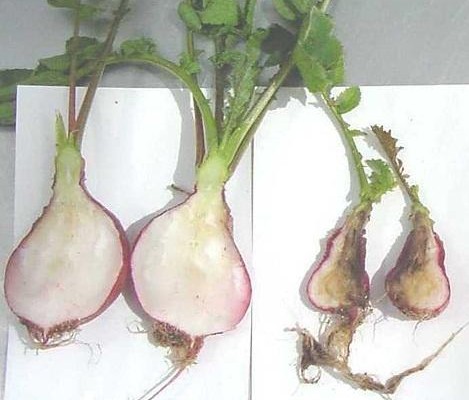
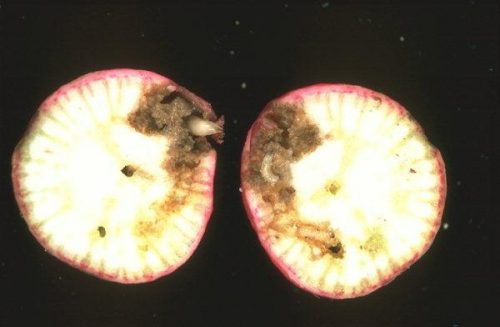
Club root (Plasmodiophora brassicae)
It is an easily recognizable disease because of the symptoms that appear on the leaves and roots. The aerial symptoms are represented by plant dwarfing, yellowing, and wilting of the leaves. On the roots the disease shows swellings or strangulations, indicating a dysfunctional root system. The disease can start as early, from the seedling stage.
Prevention and control measures:
- checking the seedlings before planting;
- choosing neutral or slightly alkaline soils for planting;
- soils can be treated with specific products to correct the pH if it is acidic;
- removing diseased plants from the crop;
- correct rotation (radish crop can return to the same land after 3-4 years);
The main pests of radishes
Aphids
They are polyphagous species, migrating from one plant to another or from one species to another. Thrips grow on spontaneous flora and then move on to cultivated species. They appear as a colony on the underside of leaves, on flowers or inflorescences, and on young shoots. Attacked plants stagnate, turn yellow, and become susceptible to fungal attack. After feeding on the plant sap, the aphids cover the leaves with their sweet droppings, forming the so-called “honeydew”, which allows saprophytic fungi to settle and form sooty mold.
Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments;
- using sticky traps.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
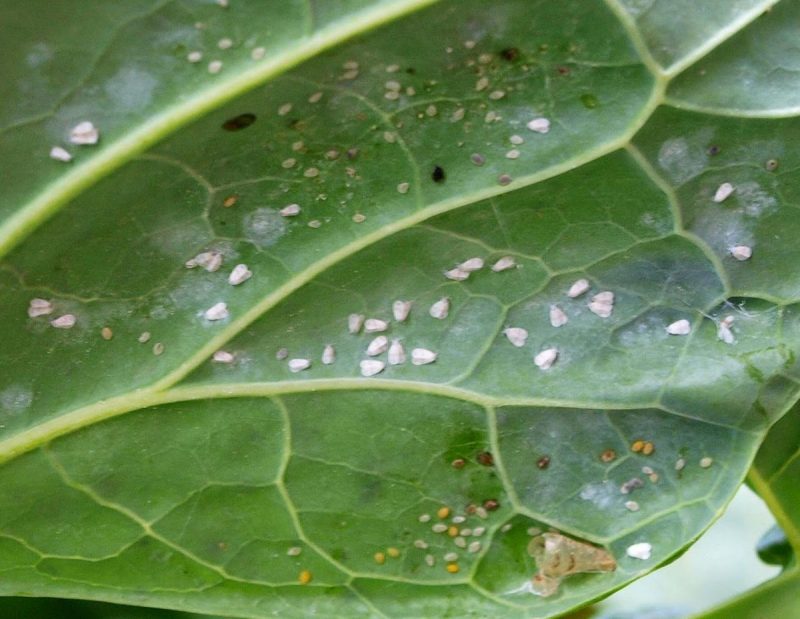
Greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum)
The pest thrives in greenhouse conditions all year round, and in the field only in summer. In the greenhouse, it can develop 3-6 generations when conditions are favorable. Adults and larvae colonize leaves, often also the shoots. Following the attack, leaves turn yellow, dry out, and fall off.
Control methods:
- using sticky traps;
- specific insecticide treatments;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Cabbage moth (Pieris brassicae)
Larvae of the cabbage white butterfly attack cauliflower, cabbage, radish, and other cultivated and wild crucifers. In the early stages, the larvae gnaw the lower epidermis and parenchyma of leaves and later consume the leaves, leaving only the veins intact.
Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Crucifer flea beetle (Phyllotreta spp.)
The adults appear in early spring, and after feeding they lay their eggs in the soil, near cabbage plants, cauliflower, kohlrabi, etc. The adults attack the leaves, gnaw the tissues, leaving the leaves with a pitted appearance.
Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments;
Slugs
It is a polyphagous species that attack many vegetable plants, flowers, vines, etc. In vegetable crops, the slug causes significant damage by perforating leaves and digging cavities in the flowers.
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with specific molluscicides;
- traps;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella)
It has several generations per year and overwinters as a pupa in the soil or on various plant debris. The adults lay their eggs on the underside of the leaves. Larvae gnaw the epidermis and parenchyma. The leaves have a leathery appearance. It attacks all plants of the Brassicaceae family.
Control methods:
- weed control;
- gathering plant debris after harvesting;
- specific insecticide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Turnip root fly (Delia floralis)
It has 2-3 generations per year and overwinters as a pupa in the topsoil. The adults emerge in spring and lay their eggs in the soil, near the plants. The larvae penetrate the plant tissues, where they burrow feeding galleries. In case of a strong attack, this pest can cause significant damage.
Control methods:
- gathering plant debris after harvesting;
- correct autumn ploughing;
- treatments during vegetation with specific insecticides;
Cockchafer (Melolontha melolontha)
It is a polyphagous species and has a generation every 3-4 years. The larvae develop in the soil and feed on the roots of plants. The adults are not dangerous to radish crops.
Prevention and control measures:
- specific insecticide treatments.
Wireworms (Agriotes spp.)
Wireworms represent the larval stage of insects of the genus Agriotes. The larvae are polyphagous, creating galleries in the roots and stem, feeding on their contents. In case of a severe attack, wireworms can compromise the entire crop.
Prevention and control measures:
- using treated seeds;
- gathering plant debris after harvest;
- correct execution of agrotechnical works;
- specific insecticide treatments;
- soil disinfection.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
European mole cricket (Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa)
It is a polyphagous species, which has an omnivorous diet, feeding on plant substrate, live prey (earthworm and various larvae), or insects. It causes damage by gnawing seeds or the plant root system.
Control:
- specific insecticide treatments.