Radishes, information about crop management

Radishes (Raphanus sativus L. Conv. radicula Pers.) it is cultivated for tuberous roots, and used for fresh consumption. The tuberous roots of radishes are rich in carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and volatile substances, and the therapeutic effects of radishes make them one of the most consumed vegetables in the spring. Radish plants are native to China, Japan, the Mediterranean basin, and the Atlantic Ocean. It is currently grown in Europe, Asia, and America.
The edible part of the plant results from hypocotyl thickening. The tuberous roots are small, round elongated, white, red, or bicolor. The edible part begins to form as the leaves grow and usually lasts for a month. The leaves are large, pubescent, toothed, and petiolate. The flowering stem is formed in the first year, can reach 1 m in height, is strongly branched, and bears racemes-type inflorescences. The flowers are white, type 4. The fruit has a sharp tip, inside which there are 4-5 globular seeds, brown-purple.
Climate and soil requirements
The plant is cold-hardy, with seeds germinating at temperatures of 2-3℃. The optimum temperature during the growing season is 16-18℃ during the day, lower at night. Radishes have high moisture requirements and lack of moisture leads to stagnant root growth, spongy root formation, and an accentuated pungent taste. The lack of light also prevents root thickening. Under long-day conditions and high temperatures, the plant develops a flowering stem rather than thickening roots. Prefers light-textured, humus-rich, loamy, neutral pH soils.
Cultivation
Radish cultivation in the field
Crop rotation
Radishes are used in successive crops, being sown before or after the main crops. It is usually practiced in spring cultivation (before the main crop) and autumn or summer cultivation (after the main crop). The best results are obtained after vegetable crops such as cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, or aubergines.
Soil preparation
The land must have good exposure and sufficient light. It is also recommended to grow on light, well-drained soils, as radishes are sensitive to excess moisture in the soil. Soil preparation can start in autumn, with removing the remains of the previous crop, fertilizing with organic and chemical fertilizers, and plowing. Dosages are indicative and should be determined based on soil analysis. Before sowing, the soil should be tilled to encourage uniform seed germination.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Culture establishment
Seed sowing can be done in spring, as soon as it is possible to enter the field, until the beginning of April, so that the plants can benefit from lower temperatures needed to form edible parts. Long days with high temperatures are favorable for flower stem formation.
The crop can be established on the entire desired area or smaller areas at intervals of 10-12 days for staggered harvesting. For maintenance and harvesting, it is recommended to sow in strips of 6 rows, 15-20 cm between rows, and 1-2 cm deep.
About 15 kg of seed is used for one hectare of land. Before sowing, the seeds can be treated.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Pest and disease control
It is done by applying treatments with approved fungicides or insecticides. To avoid the appearance of diseases or pests resistant to pesticides, it is recommended to alternate products. Use products with a short preharvest interval because radish plants have a short growing season.
Weed control
It is carried out by hoeing and it is not recommended to apply herbicides after the plants have sprouted, as the radishes have a short vegetation period.
It is recommended to irrigate radish crops to obtain high-quality yields but excess water is harmful for edible parts. Frequent irrigation with smaller amounts of water can be applied to ensure a constant supply and avoid alternating dry periods with excess water. It is recommended to use drip irrigation systems.
After full sunrise, thin out radish plants (if necessary), to achieve a distance of 4-5 cm between plants at a time.
As a rule, basic fertilization is sufficient to supply the plants with the necessary elements, but unfavorable environmental conditions may hinder the absorption of certain elements. When the plants are big enough and have already a few leaves, foliar fertilization can be carried out with specific products.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Harvesting
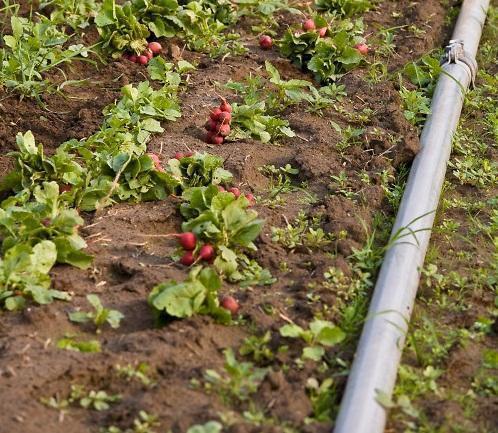
Plants can be harvested about 25-30 days after sowing. The operation is carried out in stages or a single pass when the roots have reached commercial maturity. After harvesting, the roots should be washed free of impurities and grouped in bundles, with leaves, this being the main marketing method.
Radishes cultivation in protected areas
The same principles of crop rotation and soil preparation, as well as sowing distances, are followed when growing radishes in protected areas.
However, crops can be planted from autumn, after the main crops have been removed, and until spring, at the beginning of April. For short periods, the radishes can also tolerate slightly negative temperatures. To maintain higher temperatures, protective tunnels can be installed inside polyhouses. In this case, too, staggered sowing is recommended to extend the harvesting period.
With these crops, special attention should be paid to daily aeration, as excess moisture can lead to root rot. Ventilation it can be done in the middle of the day when the outside temperatures are higher. In the spring, on sunny days, the ventilation can be done for several hours during the day, otherwise, there is a risk that the temperature in the protected areas will reach high values, leading to the depreciation of the edible part.
Water the plants when necessary, to maintain constant moisture in the soil, but not in excess.