Kiwi, planting, growing and harvesting

Kiwi, kiwifruit, or Chinese gooseberry (Actinidia deliciosa) is a plant that belongs to the Actinidiaceae family, native to Asia. Kiwifruit has spread to other parts of the world since the 19th century and is now grown in France, Greece, Chile, Spain, Australia, Italy, the USA, etc. It is cultivated for its fruits, but can also have a decorative role. The fruit contains vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, calcium, folic acid, phosphorus, potassium, and carbohydrates.
Botanical characteristics
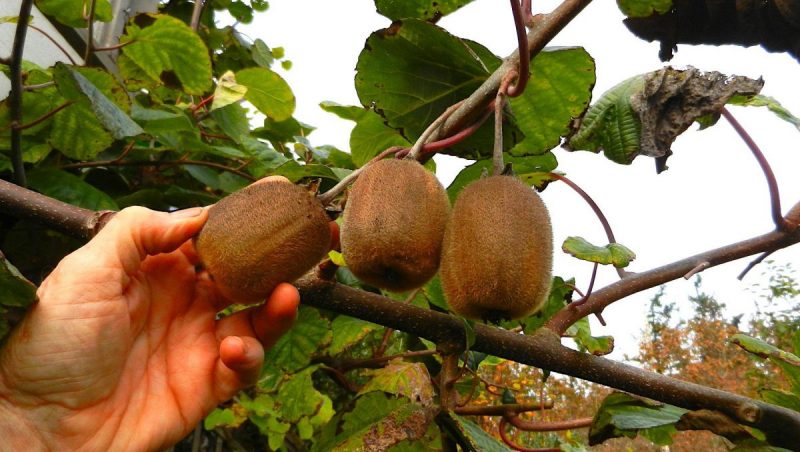
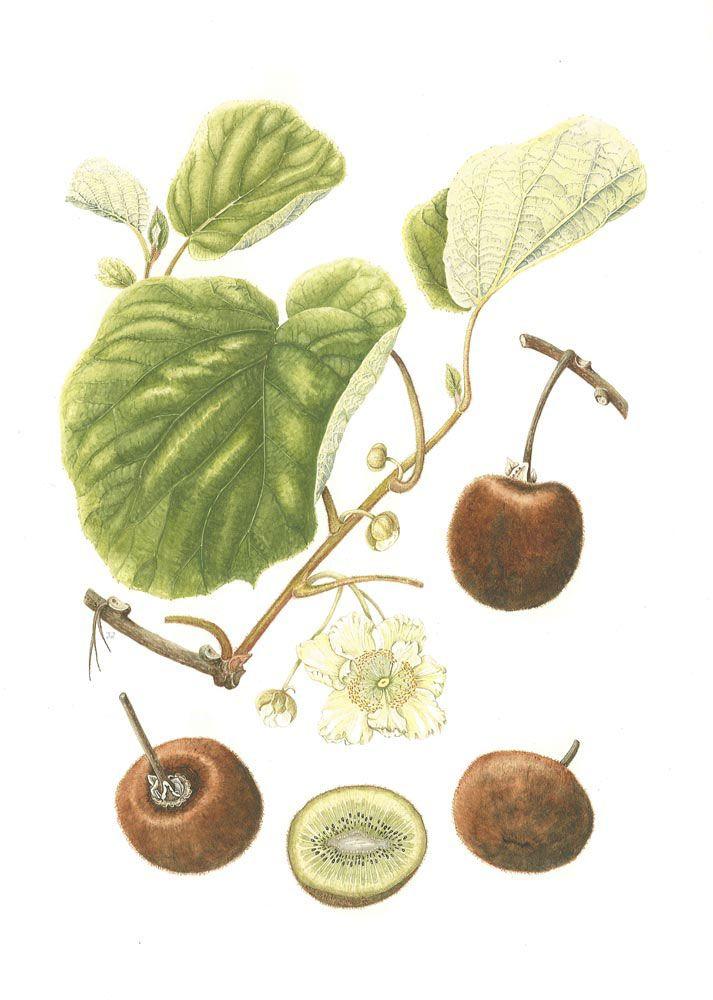
The plant grows as a vine, between 5 and 7 meters long. The leaves are large, dark green, glossy. The young leaves are covered with red leaf hairs and the mature ones with dark green hairs. It is a unisexual dioecious species. The flowers are large (2 – 5 cm), white, and develop in the leaf axils. The fruit is oval, 6 – 7 cm long, covered with a brown, pubescent peel. Flowering takes place between May and June. Kiwifruit plants are not self-fertile, but modern genetic engineering has created self-fertile varieties (e.g. Jenny). The flesh of the fruit is firm and can have different colors, from green to yellow.
Environmental requirements
Temperature is a limiting factor for kiwi cultivation. It is a frost-sensitive species and should be grown in areas where the risk of frost is low. Kiwifruit has a long vegetation period and prefers long autumns and warm springs. Regarding the light conditions, the requirements are medium to high. It can be planted in sunny places or on lands with southern exposure. This species is sensitive to soil moisture, drought or excess moisture can affect its vegetation. It is recommended to use a micro-sprinkler irrigation system to effectively control the soil moisture. Kiwi fruit grows and develops optimally on fertile soils with a high humus content, a high aero-hydric regime, and a pH between 6.5 and 7.5. It does not tolerate saline soils and those rich in carbonates.
Soil preparation
Choose the land according to the climate and soil requirements of the species. It grows well on well-lit soils, allowing it to install a support system. The species prefers fertile soil with a high aero-hydric regime and does not tolerate saline soils. Kiwifruit is very sensitive to wind action and for this reason, the land on which the future plantation will be established must be protected from strong winds. The soil should be prepared in summer, and the plots should be cleared of plant debris and plowed to a depth of 30 cm. If necessary, it is recommended to level the land and, a few days before planting, to harrow the land twice with disc harrows.
Planting
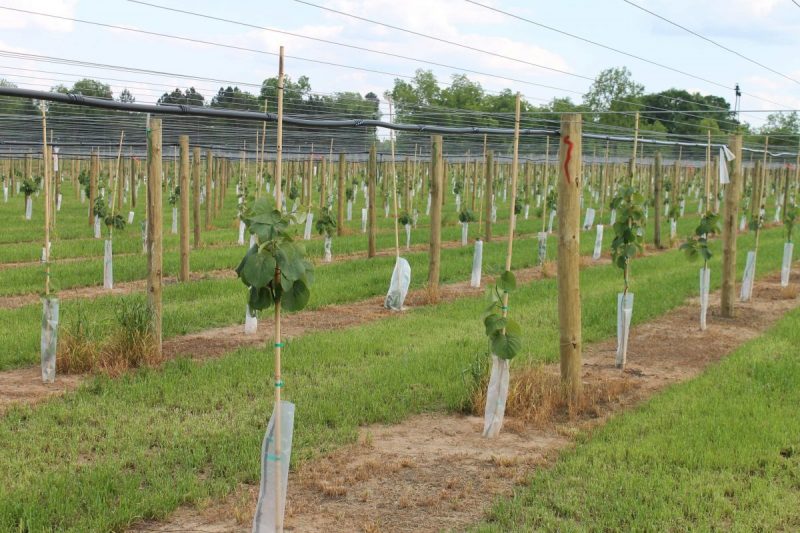
The optimal planting period is autumn or early spring when the plants are dormant. The soil should not be frozen and temperatures should be above 5℃. It is recommended the following planting scheme: 4 m row spacing and 3 m between plants per row. After establishing the planting scheme, the land can be picketed. This operation consists of marking with a stake the position of each plant on the land. It must be remembered that this species is a unisexual dioecious, and to ensure efficient pollination, the ratio between female and male plants must be 1:1. The pits can be made manually or with a drill. The recommended dimensions of the planting pits are 40x40x40 cm.
Maintenance work
In the first years, kiwi plants can be easily affected by the weeds and for this reason, the interval between rows must be kept clean. This work can be done by repeated hoeing, shallow disking, or herbicides. Herbicides should be applied locally so as not to damage the young kiwi plants. Starting with the third year, the interval between rows can be grown with perennial herbs, which should be mowed periodically, when they reach a height of 10-15 cm.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Fertilization
Fertilization is usually required from the third year. In the first years, the kiwi plant grows normally, but from the third year onwards, the plants need additional fertilization. Kiwifruit reacts favorably to fertilization with organic fertilizers.
Irrigation
It is mandatory, as plants are sensitive to this growth factor. Frequent irrigation is recommended to keep the humidity at a constant level because plants cannot tolerate drought or neither excess humidity. Micro-sprinkler irrigation methods are recommended. This method of irrigation also helps to control atmospheric humidity, as kiwifruit prefer high humidity levels.
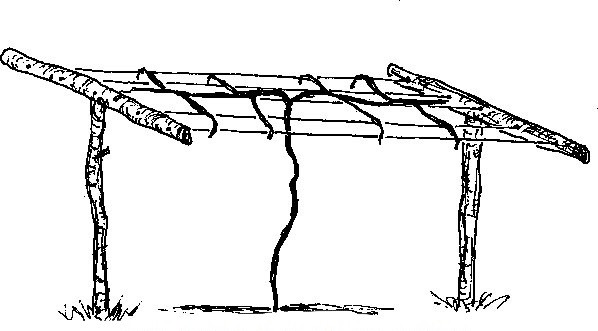
The support system
Due to the botanical particularities of this species, the crop needs additional support. It is recommended to use a T-shaped pole system with 2-3 wires. These should be about 2 – 2.5 meters high and should be inserted into the soil at a depth of 60 cm to allow the plants to be about 2 meters above the ground.
Pest control
Generally, kiwifruit is resistant to diseases and pests. Because of this, it does not require phytosanitary treatments and grows well, without being affected by biotic factors.
Pruning
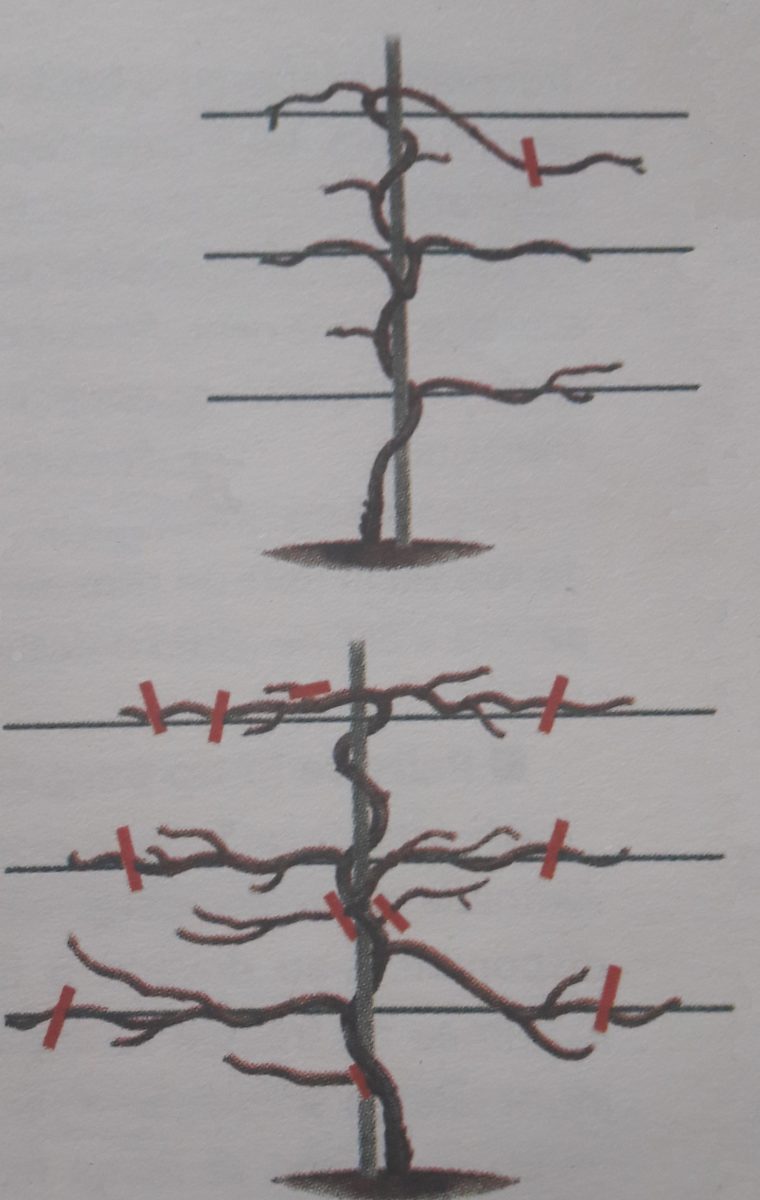
Pruning is an important operation in kiwi cultivation technology. The operation must be performed in early spring or during the vegetative growth period. Immediately after planting, shorten the vines to a height of 30 – 40 cm to ensure vigorous growth. When the central axis has exceeded one meter in height, suppress the top of the central axis to favor lateral branching. Maintain 5-6 vigorous and well-developed side branches. During the growing season, shorten the side branches to 4 – 5 buds. The intersecting branches or those that grow towards the interval between the rows must be removed.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
From the third year onwards, the plantation will start to bear fruit. During this period, pruning aims to replace the dry fruit branches with young ones. The selected shoots will be attached to the support system. During the vegetation period, to stimulate the growth of new branches, the fruit-bearing branches must be pruned (remaining only 3-5 leaves). Once the new branches have formed, shorten to 1-2 buds. When the plants enter the old age phase, apply regeneration pruning and shorten the old fruiting shoot to 2 – 3 buds. This rejuvenation operation should be carried out over 3 – 4 years.
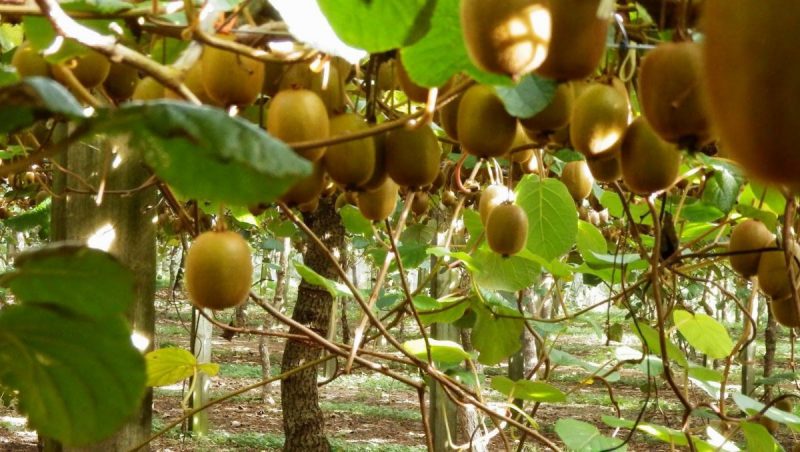
Harvesting
The fruit has to be harvested when it reaches maturity and, chronologically speaking, this period overlaps with mid-October. Kiwifruit has a long shelf life and can be stored for 3 to 6 months. The best time to eat them is when the flesh becomes soft. These fruits ripen faster if kept in the fridge in a plastic bag, next to apples or bananas.