Kiwi treatments, pest and disease control

Kiwi, kiwifruit, or Chinese gooseberry (Actinia deliciosa) is a plant that belongs to the Actinidiaceae family. It is a vine, between 5 and 7 metres long. The leaves are large, dark green, glossy. It is native to Asia but is currently cultivated in France, Greece, Chile, Spain, Australia, Italy, the USA, etc. The temperature is a limiting factor for kiwi cultivation, due to its sensitivity to frost. It can be cultivated in areas where the risk of frost is low. Kiwifruit has a long vegetation period and prefers long autumns and warm springs. It is grown for its fruit, but can also be used for decoration. Fruits contain vitamins A, C, and E, calcium, folic acid, phosphorus, potassium, and carbohydrates.
The main diseases of kiwi plants
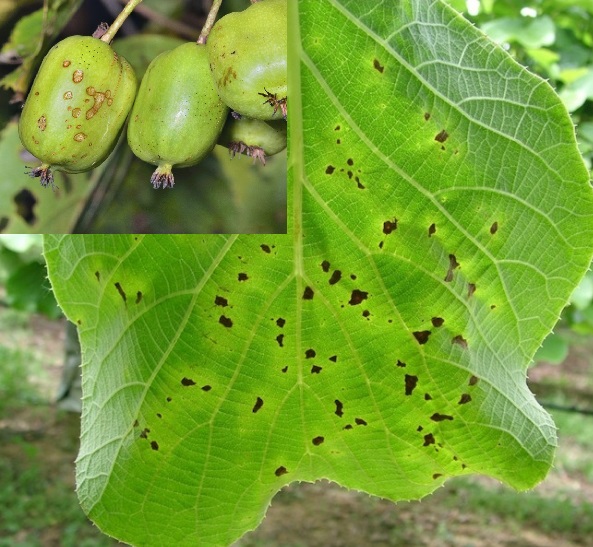
Bacterial canker of kiwi fruit (Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae)
The disease attacks all aerial organs of the plant. The first symptoms show small, well-defined, moist-looking spots. The attacked tissues dry out and fall off. Affected fruits show small brown spots, bordered by a green area. The bacterium overwinters on plant debris on the soil surface. During vegetation, the disease is transmitted by bacterial exudate, carried by various vectors (water, wind).
Prevention and control measures:
- removing attacked plants from the crop;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides.
Crown gall disease (Agrobacterium tumefaciens)
The emergence of the disease is favored by temperatures between 22 and 30 °C and atmospheric humidity of ca. 80%. Tumors of different shapes and sizes develop on the roots and stems. At first, they are small and soft, and later they become woody. This bacterium enters the tree through wounds caused by nematodes, hail, etc.
Prevention and control measures:
- disinfection of scissors and tools, when passing from one plant to another;
- pruning the affected branches and covering the wounds with wound sealer.
Root and crown rot (Phytophthora sp.)
The first symptoms include wilting and browning of the leaves. Plants have slowed growth and dry out prematurely. In the basal area of the stem, it develops lesions similar to those caused by bacterial cancer. In wet weather, the lesions become covered with a sticky fluid. This disease appears in conditions of excessive soil moisture.
Prevention and control measures:
- rational irrigation;
- avoiding soils with excess moisture.
Gray mold (Botrytis cinerea)
This disease is favored by high atmospheric humidity. The fungus appears on basal leaves and can spread to fruit and flowers if the humidity remains high. Attacked organs become covered with a grey mold and rot. The disease develops rapidly and can destroy the fruits or spread to nearby plants. Gray mold can have a severe impact on production, even after harvest.
The main pests of kiwi plants
Nematodes
They overwinter as adults inside affected plants and in the soil. They live inside affected plants and feed on sap. After the attack, the roots are deformed and the young leaves’ growth is reduced. Attacked flowers remain undeveloped or even deform.
Control methods:
- using healthy planting material;
- disinfecting the soil.
Scale insects
They are polyphagous species that attack over 200 species of plants. The scale has 1-3 generations per year and overwinters as larvae on the bark of affected species. Females and larvae spread to all organs of the affected plants, including the fruit, and feed on the plant’s sap. In case of a massive attack, the shields that protect the body of the insect overlap and suffocate the plants. The affected trees and shrubs stagnate from growth, and after 2-3 years they dry out.
Aphids
They are polyphagous species that migrate from one plant to another or from one species to another. Aphids grow on wild flora and then move to cultivated species. They form colonies on the underside of leaves, on flowers or inflorescences, and young shoots. The insects feed the plant’s sap. In case of a severe attack, the insects will kill the plant.
Citrus flatid planthopper (Metcalfa pruinosa)
It is a polyphagous species that attacks vines, ornamental trees and shrubs, and fruit trees/shrubs. It develops one generation per year and overwinters in the egg stage in the branches of attacked plants. Adults and larvae feed on the plant’s sap, inhibiting plant growth and spreading numerous viruses. Fighting this species is difficult due to the wax layer covering the insect’s body. For this reason, the planthopper can quite easily be confused with the woolly apple aphid (Eriosoma lanigerum).
Mites
They are insects that are difficult to see with the naked eye. Mites are polyphagous species that attack many plants and fruit trees, both cultivated and wild species. They feed on plant’s sap. After the attack, the leaves look parched, the flowers abort and the plant stagnates in growth.