Fruitworms – pest management

The codling moth – Cydia pomonella
Description. The adult is a small butterfly, 10 mm long. The color of the body and wings is gray-brown. The forewings are narrow, dark gray. The egg is disc-shaped, white-green in color, and is laid isolated on leaves and shoots, on branches, near the fruit. The larva is a true caterpillar, which when fully developed has a body that is 15-20 mm long.







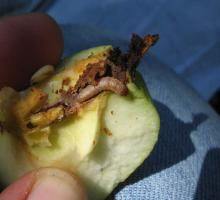
Biology and ecology. It produces two generations per year and overwinters in the fully developed larval stage, in a silky cocoon, sheltered under the bark of the trunk and in its cracks. The eggs are laid isolated, on leaves, fruits, and shoots, when the fruits are the size of a hazelnut. A female lays 50-150 eggs, the average being 50-60 eggs. Incubation lasts 8-15 days, and a few hours after hatching the larvae penetrate the fruit, either from the side or from the peduncle or calyx.
Attacked plants and damages. The codling moth mainly attacks the apple and the pear trees, but sometimes it also attacks the quince, the walnut, and the plum trees. The larvae drill galleries in the pulp of the fruit, consuming the seeds and passing from one fruit to another. The first-generation larvae attack the young fruits, the size of a walnut, and the second-generation larvae attack the mature fruits. From the gnawed galleries seeps sawdust made up of excrement and food scraps, often mixed with silky threads.
Control. It is recommended to carry out treatments with specific insecticides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The plum fruit moth – Cydia funebrana
Prevalence. The insect is widespread in Europe, North and South America, Asia Minor, and the Far East
Description. The adult is a small butterfly with a wingspan of 10-15 mm. The forewings are dark brown and have an oval, glossy, gray-brown, or leaden spot on the apex. The egg is elliptical, translucent at first, then it turns yellow. The larva has a red-bricky color on the dorsal side and pale pink on the ventral side. It measures 10-14 mm in length when fully developed.


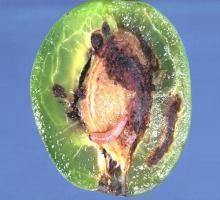
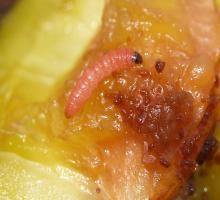
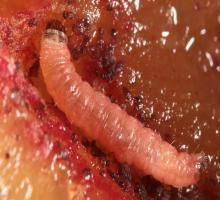
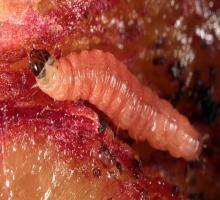

Biology and ecology. The plum fruit moth overwinters in the larval stage in a silky cocoon, under the rhytidome at the base of the stem, or in other sheltered places. It usually produces two generations per year, but in the lowland area, it develops a third generation. The eggs are laid on the underside of the leaves and the fruit. A female lays 40-80 eggs. This phase can last between 25-30 days, while the incubation lasts 6-8 days. The larvae appear on the young fruits, drill galleries, and feed on the raw pulp and seeds. The attacked fruits slow their growth, acquire a purplish color, and fall to the ground.
Attacked plants and damages. Cydia funebrana attacks both wild and cultivated plum trees, as well as cherry, peach, and apricot trees. The larvae attack only the fruit, destroying the pulp and seeds.
Control. To reduce the biological reserve of the pest, it is recommended to carry out some specific works: mount a trap around the tree trunk, catch the larvae and burn them, gather the infested fruits, to destroy or use them for other purposes.
The treatments have to be performed with specific insecticides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The European cherry fruit fly – Rhagoletis cerasi
Prevalence. The European cherry fruit fly is widespread in several countries in Europe and North America, in cherry and sour cherry orchards.
Description. The adult is a small fly, 3-5 mm long, with a black body and transparent wings, with 3 transverse stripes, wide, blackish-brown. The larva is white-yellow, it doesn’t have any legs and it reaches a length of up to 5-6 mm.


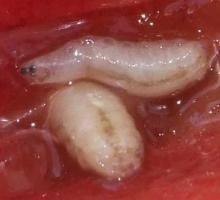



Biology and ecology. This insect produces one generation per year and overwinters in the pupal stage in the surface layer of the soil (at a depth of 2-18 cm), under the crown of trees. The first eggs are laid 1-2 weeks after they start flying. With the help of the ovipositor, the female inserts an egg under the epidermis of the fruit in the dough ripeness. The larvae appear after 6-12 days and feed on the pulp of the fruit around the seed.
Attacked plants and damages. It is the most important pest of cherries and sour cherries, the larvae of this species attacking the fruits, especially the semi-late and late varieties. The larvae feed on the mesocarp of the fruit around the seed. The attacked fruits become soft, darken and fall off.
Control. It is recommended to dig the soil under the crown of trees, in autumn or early spring to destroy the overwintering pupae. The treatments have to be performed with specific insecticides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store















































































































































































































































































































































































































































