Apple rust mite (Aculus schlechtendali) – pest management
Distribution. The apple rust mite is spread all over the globe. The increase of the biological reserve is favored by the dry and hot climate and by the small number of phytosanitary products that are efficient against mites.
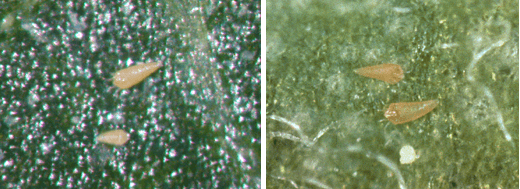
Description. Females measure approximately 0.17 mm in length and have an elongated body shape, yellow-brown. Summer females have the same number of tergites and sternites, while winter females have fewer tergites.
Life cycle. The mite overwinters as a female under the exfoliated bark of trees and in its cracks, in the scales of the buds, and at their base. In April, adults migrate from the places where they overwintered and invade the buds, leaves, and flowers. It produces 5-6 generations per year, the breeding ending in August when females appear the form in which the mite overwinters. The development of a generation takes a little time, about two weeks, depending on the temperature.
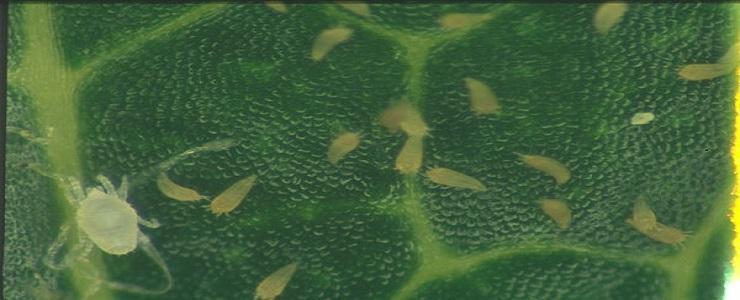
In the case of strong infestation, the number of specimens per square centimeter can reach up to 500, found especially on the leaves’ underside, where they feed.
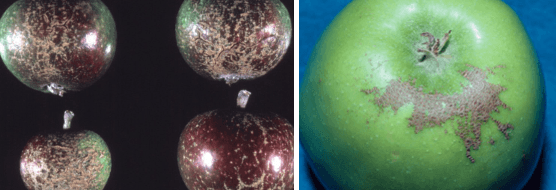
Crop damages. The apple rust mite feeds on the leaves and fruits of the attacked plants. On the leaves, after their stings, small yellow-whitish spots appear. In the case of strong infestation, the leaves acquire a silvery appearance, with reflections of lead, and the blade of the leaves rolls towards the topside, the tree thus signaling the presence of a stress factor. The leaves turn brown and fall prematurely. Another consequence of the attack is the slow growth of the herbaceous shoots and their deformation. The attack on the fruits is manifested especially in the calyx area. The attack of the mites on the growing fruits causes the appearance of coarse spots that lead to the depreciation of the ripe fruit.
Pest management. Small populations do not cause significant damage to trees and are also a source of food for natural predators (Typhlodromus pyri), which are very important in controlling mites populations. Carrying out phytosanitary treatments is recommended when exceeding the economic threshold, of 10-15 mobile insects on the leaf, in summer. Control treatments for the apple rust mite can be applied during dormancy or budding (in the pink bud stage) and during the growing season, starting in April. Adequate irrigation of trees is important because the stress caused by insufficient water intensifies the effect of the mite attack. Treatments must be performed with specific acaricides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store