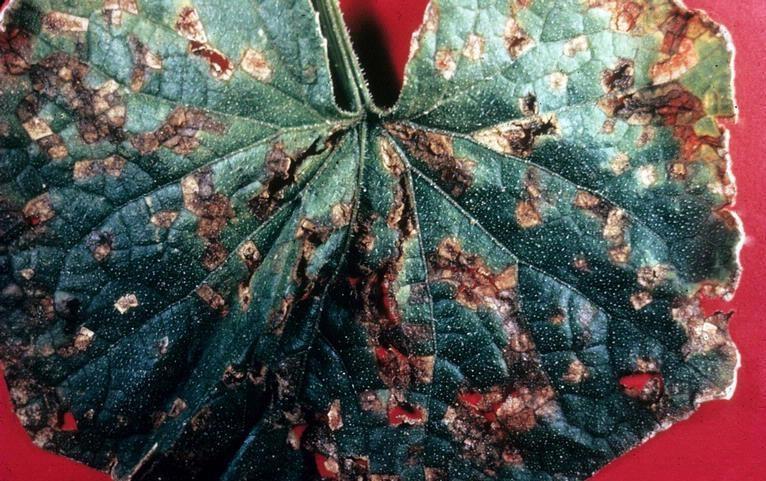
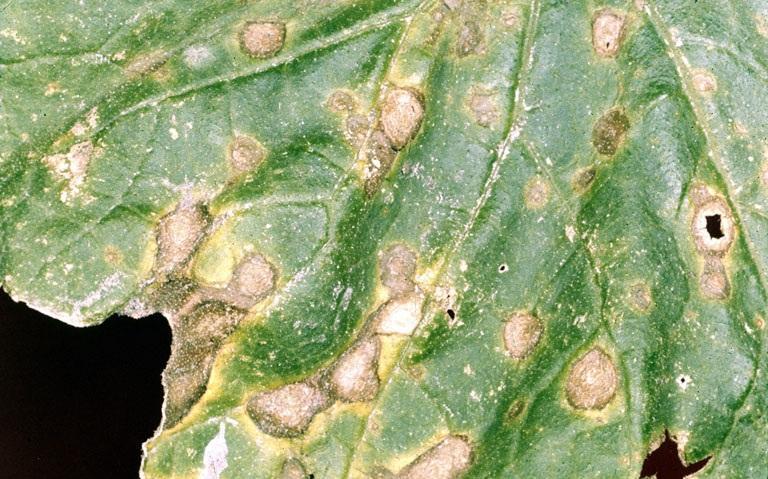
Zucchini, treatments against pests and diseases

Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo) is a herbaceous plant that belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family. It is a popular plant, being widely cultivated for its edible fruits. Its stem grows as an erect, vigorous, short-branched bush, but there are varieties with long, creeping stems. The zucchini leaves are large, with a long petiole, and the flowers are unisexual, large, and yellow. The fruit is a cylindrical melon. Zucchini is very light-demanding, and growing in shady fields reduces production. It has high moisture requirements but resists drought well due to its developed roots. It prefers deep, loose, weed-free soils, sheltered from draughts. Zucchini crops can be affected by pests and diseases, against which it’s important to apply the right treatments.
The main disease of Zucchini
Viruses
Cucumber mosaic virus
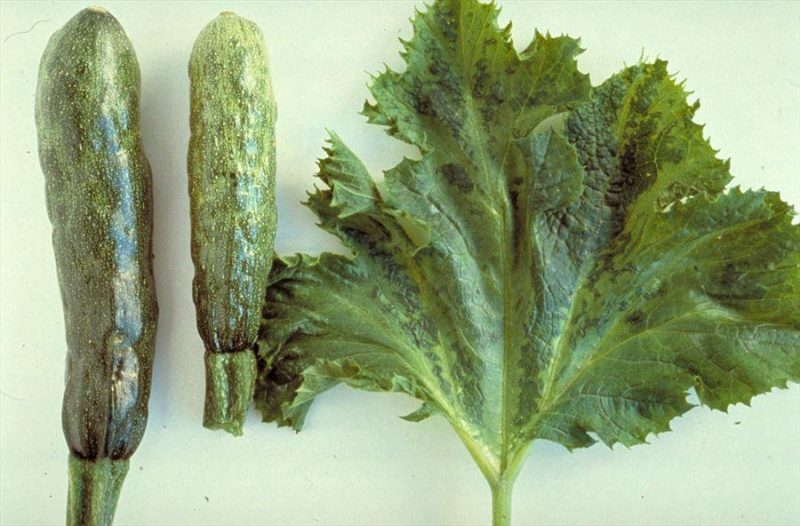
The virus is widespread, being found in zucchini, squash, tomatoes, eggplant, and peppers, as well as other species of wild plants. Symptoms include discolored spots on the leaves, giving a mosaic appearance. If temperatures are low, necroses appear on the leaves, starting from the outer edges towards the center. Affected plants produce small, deformed fruit with mosaic spots. The virus is transmitted through aphids, dodders, and infected seeds.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- destroying weeds within the crop and nearby;
- using healthy seeds;
- using resistant varieties of zucchini;
- applying insecticides to control the aphid population.
BACTERIOSIS
Angular leaf spot (Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans)
The attack occurs on all aerial organs of the plants (stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits). Small, moist, brown, irregularly shaped spots appear early in vegetation. Later, these spots turn brown and the tissue around them dries out and peels off. On the fruit, the attack results in small, circular, moist-looking spots and a whitish central area. Bacterial ooze appears around these spots (in wet weather). High humidity (over 90%) and temperatures between 18 and 28 ºC encourage the appearance of the disease. This disease is transmitted by infected seeds or by vectors (wind, irrigation, rain, agricultural tools).
Prevention and control measures:
- seed treatment before sowing;
- cultural hygiene;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- chemical zucchini treatments with specific fungicides.
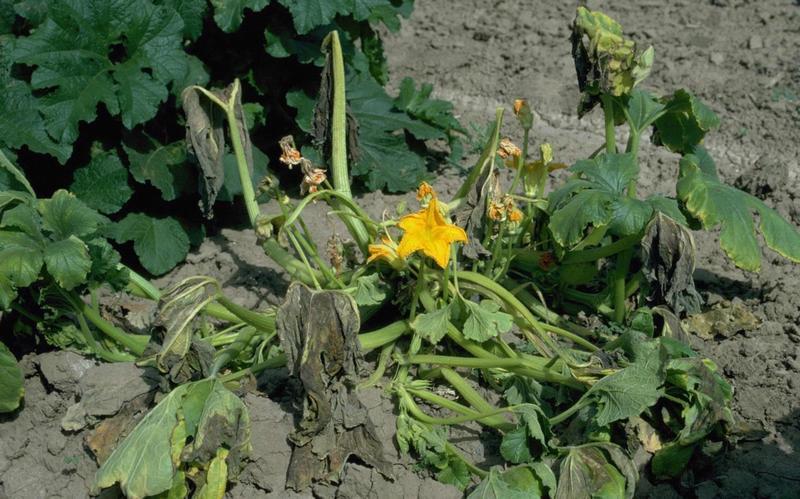
Cucurbit bacterial wilt (Erwinia tracheiphila)
In zucchini, the leaves wither in the shape of an umbrella. Afterward, the stem tissues are destroyed and the entire plant withers due to the conductive vessels blocked by the bacteria. After cutting the roots and stems, a white-grey bacterial fluid leaks from the vascular vessels. The bacterium survives on plant debris for only a few weeks but is transmitted by the striped beetle (Acalymma vittatum) and the spotted beetle (Diabrotica undecimpunctata).
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- specific insecticide treatments for insect control.
Mycosis
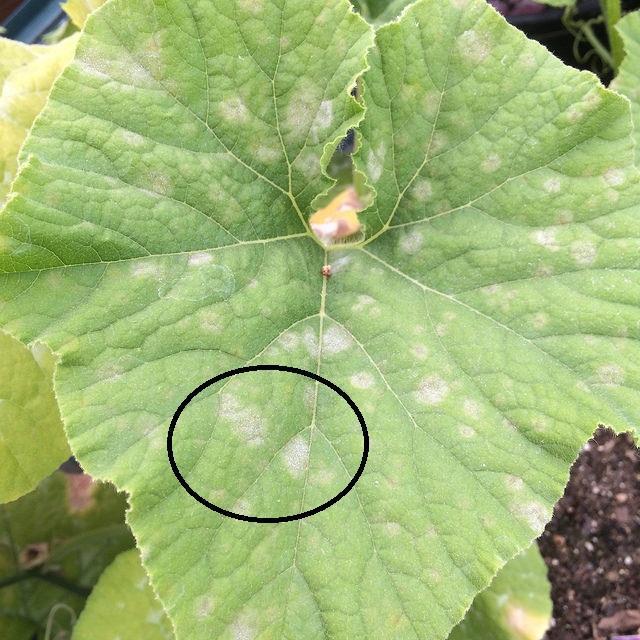
Cucurbits powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca fuliginea)
It is a common disease in cucumbers, melons, zucchini, and other cucurbits, causing significant damage. This disease is manifested by the appearance of large, white spots on the leaves, which become powdery. Heavily affected leaves turn brown, dry out, and fall off. Fungus outbreaks occur in temperatures above 24ºC and dry weather.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- growing tolerant varieties;
- chemical zucchini treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Cucurbits downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis)
It is the most important disease of cucurbits, causing significant damage to both field and protected crops. Symptoms include yellow-green spots on the upper leaves, which later turn yellow, and finally, the tissue turns brown. On the underside of the leaves, next to the spots, there appears a purple-grey fuzz made up of the fungus’ fruiting bodies. After the attack, the leaves dry out and fall off, and the fruits remain small. The disease is favored by the presence of water droplets on the leaves and temperatures between 10 and 30 ºC.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- growing resistant varieties of zucchini;
- gathering and burning of plant debris left over from harvesting;
- zucchini treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
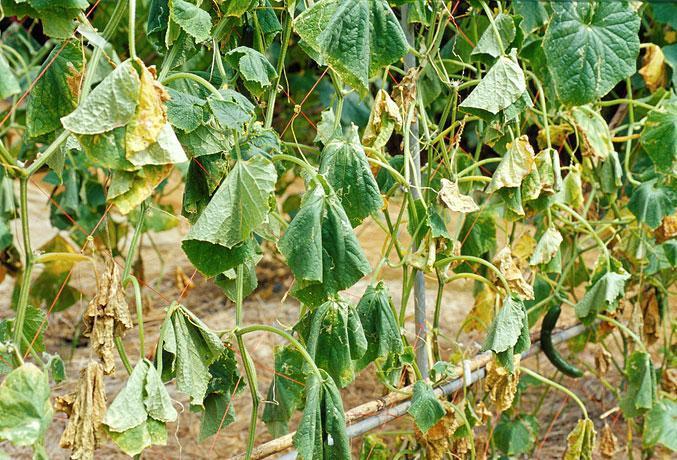
Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum)
Fusarium wilt is a vascular disease, starting with leaves turning yellow and wilting, after which the disease gradually progresses to the top of the plant. In the stem section, it can be seen that the vessels are browning. Temperatures between 28 and 32 ºC, slightly acid soil pH, high soil moisture, and low potassium levels are factors favoring the occurrence of this disease.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- disinfecting the seed substrate and treating the seeds before sowing;
- rational fertilization;
- chemical zucchini treatments during the growing season with specific fungicides.
Gray mold (Botrytis cinerea)
The attack occurs in greenhouses and polytunnels, but in years with heavy rainfall, it also occurs in the field. The most common symptom is the sudden wilting of succulent tissues (stems, fruits). On the fruit, symptoms include deep, moist, brown spots of irregular shape and size. The attack is favored by high humidity (more than 95% several days in a row), lack of ventilation, persistent cloudiness, fertilization, and excessive watering.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- rational fertilization;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
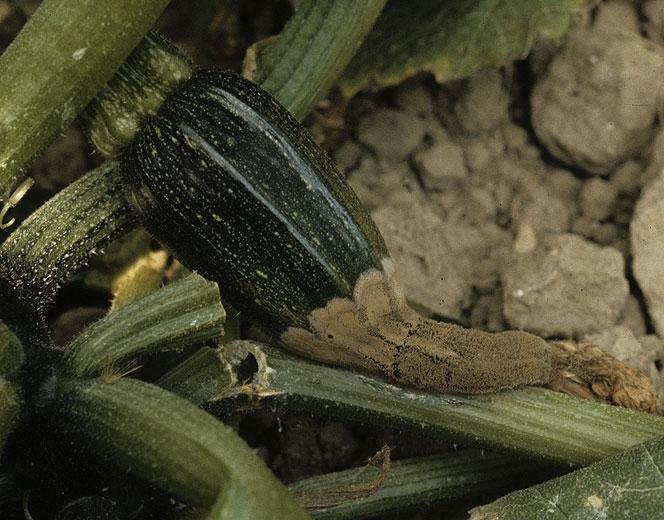
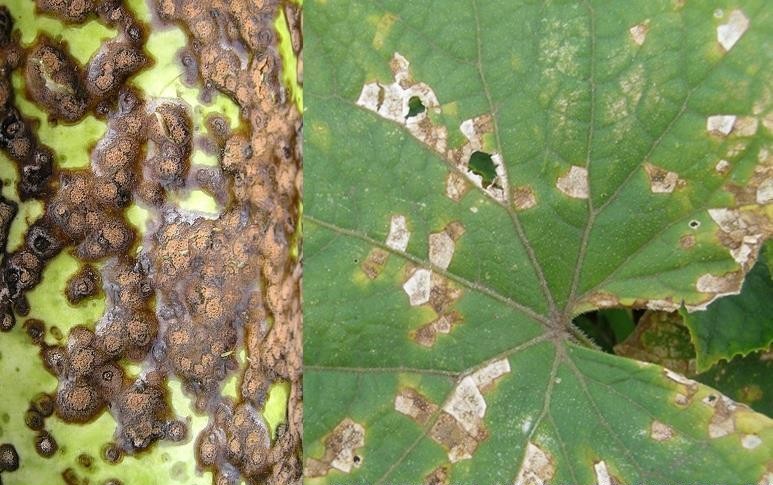
Anthracnose (Colletotrichum lagenarium)
The disease manifests itself on all aerial organs, in conditions of atmospheric humidity and temperatures around 25 ℃. Yellowish spots appear on leaves and stems, which then turn brown, affected tissues become sunken, and large, circular, brown spots appear on fruit. Over time, the spots become covered with a pink mold, and other pathogens may settle on these lesions.
Prevention and control measures:
- using healthy and certified zucchini seeds;
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- zucchini treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Damping-off (Pythium spp.)
It is one of the most important seedling diseases and manifests itself from the germination and sprouting stage to the 2-3 true leaf stage. When attacked, the tissues at the stem base blacken, become watery, and decay. This disease is favored by temperatures between 18 and 30 ºC and humidity above 90%.
Prevention and control measures:
- removing affected plants from the crop;
- substrate disinfection;
- avoiding excess watering and regular aeration of seedlings;
- zucchini treatments with specific fungicides.
Cucurbit scab (Cladosporium cucumerinum)
The disease can appear as soon as the cotyledons appear. The attack appears as greenish, colored patches, which then turn greyish, bordered by a yellow ring. The attacked tissues turn brown, dry out, and detach from the plant. Greyish, sunken spots appear on the fruit. High relative humidity and temperatures of 18-25 oC favor the appearance of the disease.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- disinfecting the hotbed substrate;
- rational fertilization;
- growing resistant varieties of zucchini;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides.
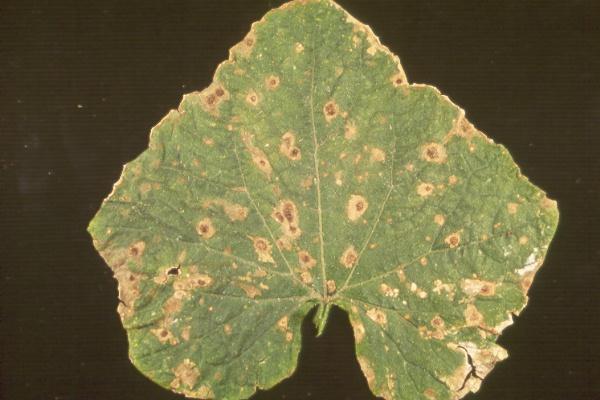
Alternaria leaf blight of cucurbits (Alternaria cucumerina)
It is a common disease of plants of the Cucurbitaceae family (cucumbers, zucchini, melons, etc.). Small discolored spots appear on the affected leaves, which may merge, while concentric areas appear on their surface, representing the fungus fructifications. The fungus survives on plant debris on top of the soil and spontaneous cucurbits.
Prevention and control measures:
- correct crop rotation;
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- weed control;
- seed treatment before sowing;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The main pests of zucchini
Wireworms (Agriotes spp.)
Represents the larval stage of Agriotes insects. Adults have a mixed diet, but the damage they do is insignificant. The larvae attack the root system and the plant’s stem, causing them to dry out.
Prevention and control measures:
- disinfecting the soil before planting;
- applying soil treatments with specific insecticides when planting.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
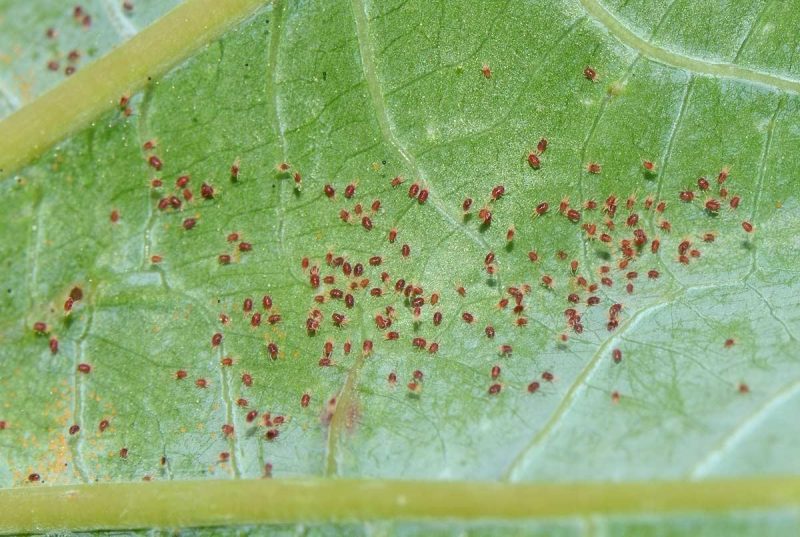
Red spider mite (Tetranychus urticae)
It has 6-10 generations per year and overwinters as an adult, mostly as females (males are generally rarer), under the peeling bark of trees, under fallen leaves, on dry weeds, or in the topsoil. Attacked leaves dry up and fall off, causing significant damage. The attack results in stunted growth and premature fruit ripening.
Control measures:
- carrying out treatments with acaricides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
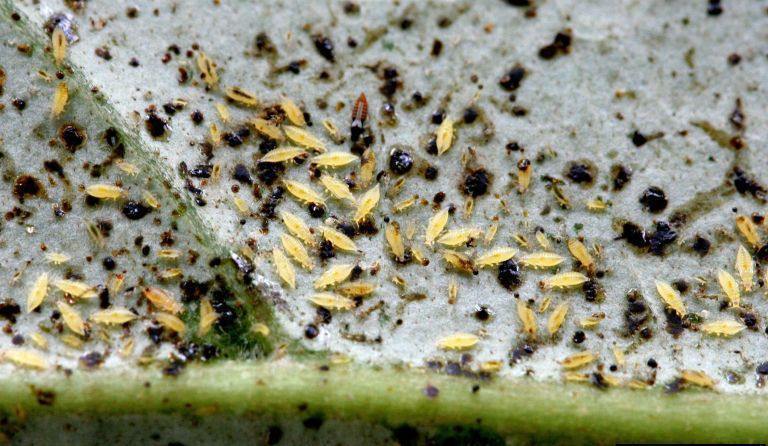
Aphids
They are polyphagous species that migrate from one plant to another or from one species to another. Aphids grow on spontaneous flora and then move to cultivated species. They appear as colonies on the underside of leaves, on flowers or inflorescences, and young shoots. Attacked plants stagnate, turn yellow, and become susceptible to fungal attack. Aphids feed on the plant’s sap and then cover the leaves with their sweet droppings, forming the so-called “honeydew”, which allows saprophytic fungi to settle and form sooty mold.
Control measures:
- using sticky traps;
- specific insecticide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
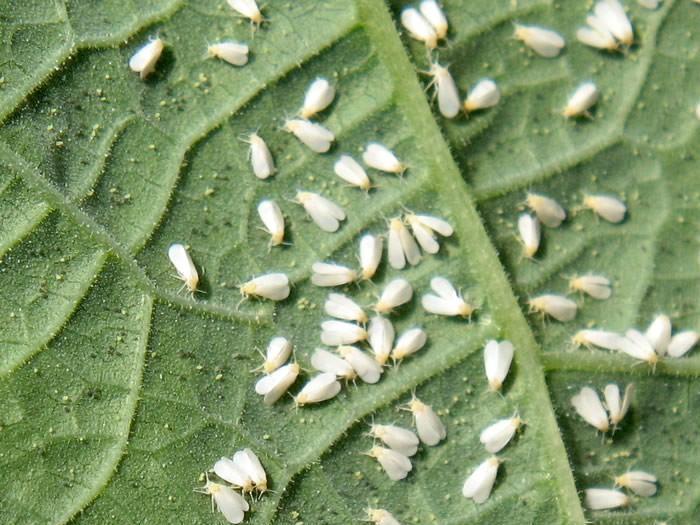
Greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum)
The pest grows in greenhouse conditions all year round, and in the field only in summer. In the greenhouse, it can develop for 3-6 generations when the conditions are favorable. Adults and larvae colonize the leaves, often the shoots. Following the attack, the leaves turn yellow, dry out, and fall off.
Control measures:
- destroying plant debris after harvesting;
- disinsecting greenhouses and polytunnels before establishing a new crop;
- using sticky traps;
- specific insecticide treatments.
Thrips
They are small pests, difficult to see with the naked eye, which attack a large number of cultivated plants. They colonize the growth tips, flowers, and leaves, causing flower abortion and plant dwarfing. Thrips are also vectors for virus transmission.
Control measures:
- using sticky traps;
- specific insecticide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store