Tomatoes, information about crop management

Tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum) are grown for their fruit, which is eaten when physiologically ripe, but also raw for pickling. Tomato fruits are eaten fresh, prepared, or canned and are rich in vitamins, sugars, amino acids, and organic acids. The chemical composition is influenced by the variety, the soil and climate conditions, and the technology applied.
Tomatoes are native to Central and South America. In Europe, they were first cultivated in Spain, Portugal, and Italy. In China and Japan, tomatoes arrived in the 16th century. Today, tomatoes are among the most widely cultivated vegetable species. Commercial tomato cultivation began in France in 1880.
Botanical particularities
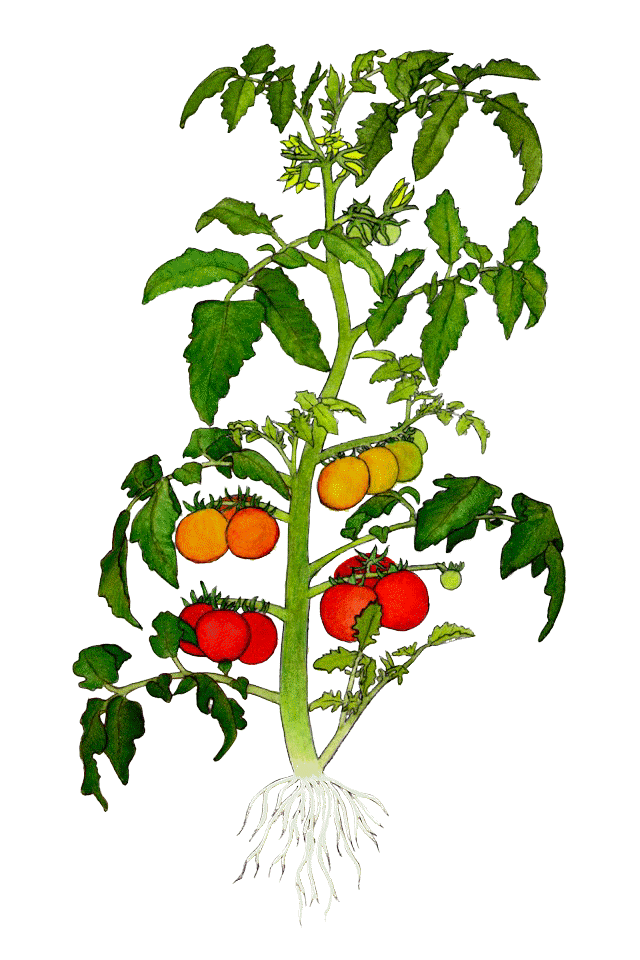
Tomato root penetrates 1.5 m into the soil and has numerous lateral branches. They grow rapidly, depending on soil temperature. The stem can have indeterminate, semi-determinate, or determinate growth, depending on the variety. Tomatoes can form many offspring, which are removed in certain varieties, depending on the type of growth.
The plant’s leaves are divided, with leaves of different sizes, arranged alternately. Its leaflets are ovate-lanceolate in shape. The inflorescence is cyma-like and appears on internodes. Tomato flower is type 5, yellow, self-pollinating. Its fruit is a berry type, of various shapes, sizes, and colors. Tomato seeds are elongated oval, with silver hairs.
Climate and soil requirements
Tomatoes are thermophilic plants, being sensitive to low temperatures. Seeds germinate at temperatures above 10℃, with an optimum of 22-24℃. The root develops optimally at temperatures between 26 and 32℃. Alternating temperatures of 14℃ at night and 25℃ during the day, while the seedling is growing, leads to an increase in the number of inflorescence flowers. If the temperature at night is high, vegetative growth is more developed. The optimum growing and fruiting temperatures in tomatoes are between 17 and 23℃.
Light
It plays an important role in tomatoes’ growth and fruiting. Plants develop normally when the light intensity is between 3000 and 6000 lux. Insufficient light in the seedling phase leads to poor seedling development and etiolation (elongation).
In the fruiting phase, insufficient light leads to poor fruit sets and reduced yield. If there is little light during the ripening phase, the process is prolonged. For crops grown in protected areas, additional lighting is required, or hybrids for extra-early crops.
Humidity
Tomato plants have moderate moisture requirements, but for high yields, regular irrigation is recommended. Watering frequency and the amount of water applied are related to environmental factors. In hot periods, crops must be irrigated even daily, preferably by drip irrigation systems. The optimum time for watering is early morning. During the fruiting period, alternating periods of drought with excess water lead to fruit cracking. Tomatoes prefer relative humidity values of 50-60% to avoid fungal diseases such as grey mold, downy mildew, etc.
Fertilization
Fertilization is an important link, as plants have high nutrient requirements. The need for nutrients is higher during the flowering and fruit set, as well as during their growth and maturation. If during the vegetative growth period, the plants need higher amounts of nitrogen after the plants begin to bear fruit, the need for phosphorus, potassium, and other elements increases.
Nitrogen plays an important role in the plant’s vegetative development and also in fruit production. Nitrogen deficiency is manifested by the formation of thin tips with small leaves. Phosphorus has a role in root development, stimulating flowering and assimilating nitrogen. Insufficiency of phosphorus causes flower abortion, low fruiting, the leaves have a purple hue and fruit cracks. Tomatoes consume large amounts of potassium, especially during fruit growth and ripening, with effects on fruit quality and plant disease resistance.
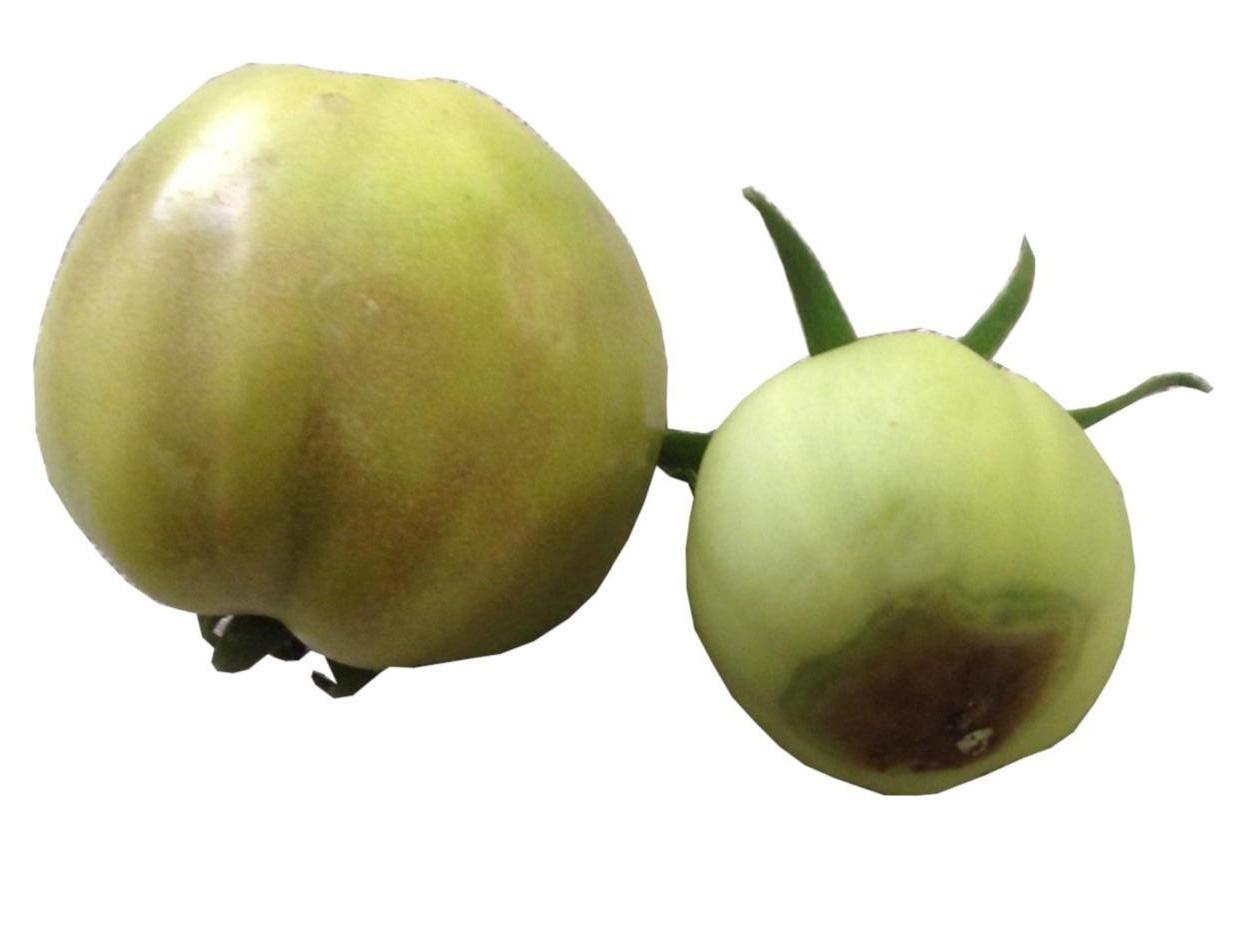
Calcium plays a role in root development and cell wall formation, with effects on fruit quality.
The first symptoms of calcium deficiency can be observed on the fruit, by the appearance of a rotten area in the calyx area (at the top of the fruit), and later, fungi of the Alternaria genus can appear on this area.
To supply the plants with the elements necessary for growth and fructification, it is recommended to apply root and foliar fertilizers.
Soil
Tomatoes grow well on loamy, mineral-rich soils with a high humus content, with an optimal aero-hydric regime, and do not prefer heavy, clay soils. Flatland with shallow groundwater, no weeds, and a low acid pH is suitable. Air plays an important role in tomato cultivation. Increased CO₂ concentration in the air in protected areas (greenhouses, polyhouses) leads to significant yield increases.
Cultivation
TOMATO CULTIVATION IN THE FIELD
Crop rotation
Tomatoes can be grown after alfalfa, beans, peas, onions, garlic, cucumbers, melons, zucchini, and some root vegetables. This crop should not return to the same land for 3-4 years, as monoculture leads to yield decreases and increased incidence of diseases and pests. Choose wind-sheltered, flat, irrigable land.
Soil preparation
This work is carried out from autumn and starts with basic fertilization with organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers, depending on the soil supply. Fertilizers can be incorporated into the soil with the plowing. Dosages should be determined after a soil analysis. In spring, fertilizers with higher nitrogen content, or balanced fertilizers should be applied, but not before a pH test.
Before planting, pre-emergent herbicides can be applied, depending on the specifications of each product. The ground can be modeled in ridges or raised layers, to allow the ground to heat up faster.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Seedlings planting
Tomatoes can be grown in greenhouses or hothouses. Sowing is done sparingly, in rows 5 cm apart and 2 cm between plants per row. For one hectare you can use 250 g of certified seed, pre-treated. It is not recommended to use seeds harvested from previous crops as they may carry diseases.
To facilitate germination, seeds can be kept moist using specific products.
The substrate in which the seeds will be sown must be of good quality, preferably free of diseases, pests, and weed seeds. A mixture of garden mold soil, peat, and leaf compost can be used, but in this case, the substrate must be disinfected with specific products.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
After sowing and sprouting, you can carry out treatments with approved fungicides to reduce the risk of damping off.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Once the first two true leaves appear, the seedlings should be transplanted in pots or trays. A week after transplanting, you can carry out foliar fertilization with specific fertilizers, depending on the needs of the plants, to supply them with the elements necessary for growth. Label specifications should be followed depending on the product chosen.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The seedling age at planting should be 45 days, and the seedling should be healthy and vigorous, with short internodes. Seedlings must be watered well one day before planting and 1-2 weeks before they are hardened. This procedure involves opening the windows of the nursery/polyhouse in the morning and closing it in the evening. In the last week, the windows should be left open during the night, so that the plants can acclimatize to the new environmental conditions.
Planting
The optimal planting time is between 1 and 25 May. If you want to establish a summer-autumn crop, the seedlings can be grown in unheated seedbeds or unheated ponds, or even in the field and planting can take place during June. Crops intended for industrialization, established with varieties and hybrids with determined growth, can be sown directly from mid-April to early May, depending on climatic conditions. It is recommended to sow in staggered 10-day intervals to harvest the cultivated area at the right time.
Before planting, the tomato seedlings must be watered by dipping the pot in a solution of a fungicide specifically designed to control damping-off. Follow the recommendations on the label, depending on the product chosen. For subsequent watering, a drip irrigation system can be installed before planting. The seedlings must be planted 10-15 cm deep, 70-100 cm apart, and 30 cm apart per row, depending on the variety. After planting, watering is recommended and at the same time, fertilizers should be used to stimulate rooting. At the next watering, you can apply a product to improve fertility and soil structure and to create better root absorption conditions.
Pest and disease control
It is done by applying treatments with approved fungicides or insecticides. To avoid the appearance of diseases or pests resistant to pesticides, it is recommended to alternate products.
Weed control
It can be done by repeated hoeings, which destroy weeds and keep the soil loose. Weeds can also be controlled chemically by applying herbicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Care works
Tomato varieties with semi-determined and indeterminate growth need a support system. In field crops, the plants can be supported with stakes, placed next to each plant, or with a trellis support system, which allows the plants to be tied vertically with string.
A very important work in tomato growing technique is suckers pruning. The operation consists in removing the lateral shoots (suckers), that appear at the leaf axils. If they are left on the plant, the sucker’s growth leads to reduced production, as they consume the resources the plant needs for fruiting. Suckers must be removed when they are about 4 cm tall.
After pruning suckers, pinching off and defoliation works, it is recommended to apply curative copper-based fungicides to promote healing.
Defoliation is a work that ensures crop aeration.
Dry and diseased leaves at the base must be removed from the crop. After the fruit on the first level has reached the optimum size, the leaves on the lower level can be removed.
To maintain soil moisture and control weeds, the crop can be mulched with foil or organic material. If the mulching foil is installed along the rows, weeds in the rows can be removed by hoeing, or by applying a specific herbicide.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Mulching warms the soil and controls soil moisture, maintains a good phytosanitary condition, prevents weed growth, and reduces the number of maintenance works.
For field crops, it is not necessary to stimulate the flowers to set fruit, pollination is carried out by pollinators. If you want to stimulate the flowers to obtain larger and earlier fruits, you can use a fruiting stimulant.
Irrigation
It is carried out depending on environmental conditions and the amount of precipitation. In dry periods, irrigation can be done even daily, especially in the phases with maximum requirements (flowering, fruiting, ripening).
Fertilization
Tomato plants are high consumers of nutrients and require both root and foliar fertilizers. One to two weeks after planting, more phosphorus-rich or balanced fertilizers need to be applied to encourage rooting.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
During flowering and fruit growth, foliar fertilizers can be applied to help fruit set. Granular fertilizers can also be applied, with a content that meets the nutritional requirements of this phenotype.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Fruit ripening requires higher amounts of potassium, and products with a higher content of this macroelement can be used for this purpose.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Harvesting
Tomatoes are harvested at full maturity, when they are red, when grown in a homestead system. In commercial crops, the fruits are harvested at the fruit-ripening stage, especially hybrids that are capable of post-ripening. For preservation (pickling), the fruits are harvested raw or when it has reached the optimum size.
Usually, the harvest is done manually, in stages, during the fruit ripening. Tomatoes with determined growth, grown for processing, can be harvested mechanically.
GROWING TOMATOES IN PROTECTED AREAS
Soil preparation
It is carried out similarly to the field crop, starting in autumn, after the previous crop has been removed. As the incidence of diseases and pests is higher in protected areas, it is recommended to disinfect with specific products before planting the seedlings.
Crop establishment
It is made with seedlings produced in heated polyhouses, according to the procedure described above. The age of the tomato seedling, in this case, must be 50-60 days and the sowing work must be done depending on the time of planting. Seedlings can be planted from mid-March, depending on the heating possibilities.
Irrigation should be carried out with water at a temperature as close as possible to the temperature inside the protected space, so as not to create heat stress. Plant irrigation should be carried out by drip irrigation systems, as often as necessary, so that the plants get enough water in the growing phenotypes.
Weed control
Ideally, this should be done by hoeing or using mulch foil. In protected areas, mulch foils can be spread over the entire soil surface, having beneficial effects on the soil temperature and maintaining its humidity.
Care works
They are similar to those specified for field cultivation. Given that pollinators are not present during the flowering period, it is necessary to use specific stimulators.
Attention should be paid to the daily ventilation of sheltered spaces at the hottest times of the day. Daily ventilation should be carried out even if outside temperatures are low, to encourage gas exchange.
Pest and disease control
It is done by applying treatments with approved fungicides or insecticides. To avoid the appearance of diseases or pests resistant to pesticides, it is recommended to alternate products with different active substances.