Roses, pest and disease control

Roses (Rosa spp.) are some of the most cultivated flowering plants in the world. In addition to the decorative purpose, roses are also grown for their petals, which are used in the food or cosmetics industry. Roses grow as a dense shrub consisting of numerous perennial stems and bloom abundantly. The stems have lignified and straight, upwards-oriented thorns. The leaves are composed of 5 to 7 leaflets. They have an ovate shape, have serrated edges, and have hairs along the ribs. The petiole of the leaves is tomentose. The flowers are arranged in groups of 2-3 in the inflorescence, have a red or pink color, and the corolla is double. The fruit is false, red, with an ellipsoidal shape, called a rosehip. Being a very widespread species, it is important to know the factors that can influence their growth and development.
The main rose diseases
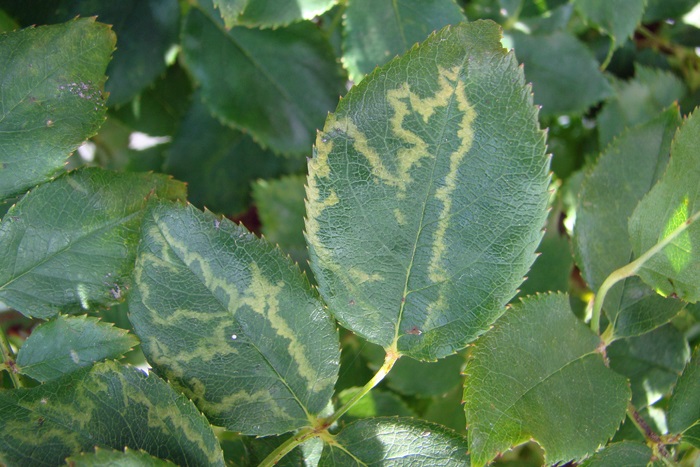
Ring spot disease caused by the Cherry necrotic ringspot virus. The symptoms of this disease are represented by yellow spots and rings. In severe cases, banded chlorosis appears along the ribs. The leaflets often become deformed. The buds of diseased plants grow poorly, and the flowers sometimes fade. The virus is transmitted through grafting or other types of vegetative propagation.
Prevention and control measures:
- the use of healthy grafting materials and parent stocks;
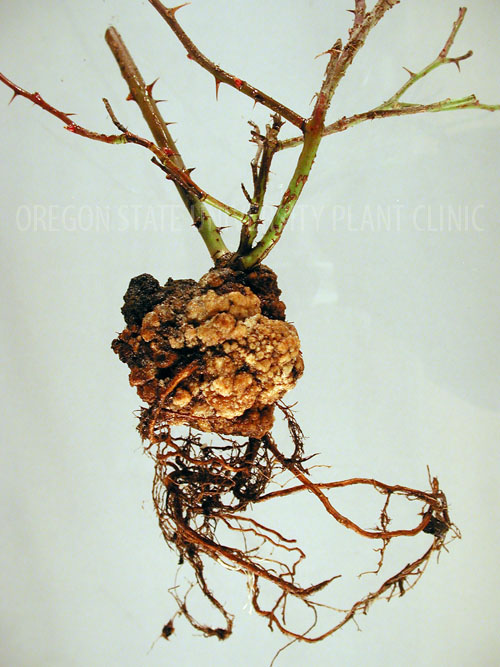
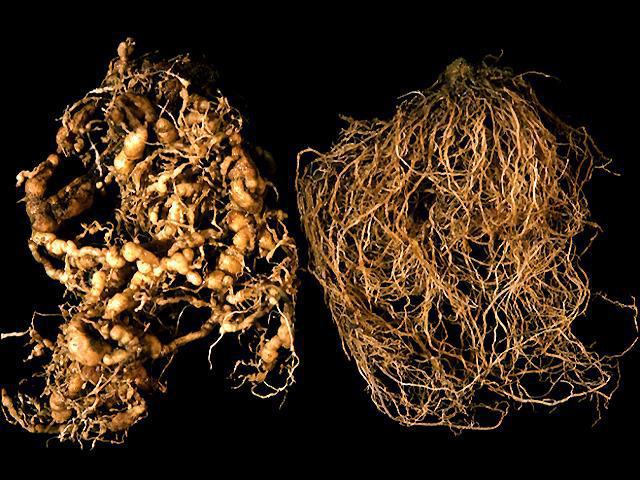
Crown gall disease caused by Agrobacterium radiobacter pv. tumefacias. Tumors develop on the roots and stems, at first small and soft, and later they become woody. Tumors have different shapes and sizes. These tumors produce masses similar to leaves, buds, or shoots. The cells that make up these tumors are large and deformed. This bacterium enters the plant through wounds caused by nematodes, hail, etc. The occurrence of this disease is favored by temperatures between 22 and 30 degrees Celsius and an atmospheric humidity of 80%.
Prevention and control measures:
- disinfection of scissors and tools, when moving from one bush to another;
- removal of affected plants;
- preventive treatments during the vegetative growth period with copper-based products.
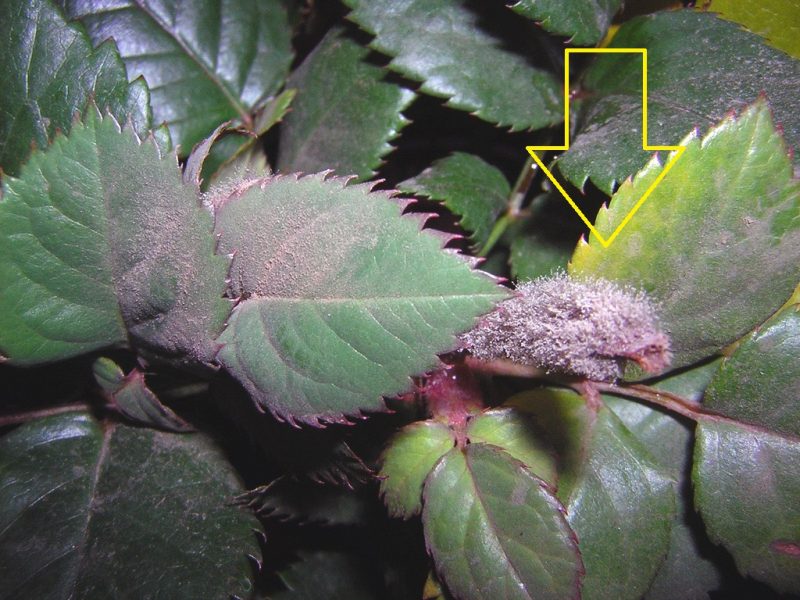
Powdery mildew caused by the fungus Sphaerotheca pannosa. This fungus affects all the aerial organs of the plant. On both sides of the attacked leaves, whitish spots of different shapes and sizes appear. The attacked tissues are necrotic, the leaves curl up, and finally dry out. The young shoots are covered with a white mycelial felt. In case of severe attack they dry out. In severe cases, the flower buds are covered with a whitish mycelium . They no longer grow or produce flowers. The attack can also manifest on the flowers, their petals showing symptoms similar to those affecting on the leaves.
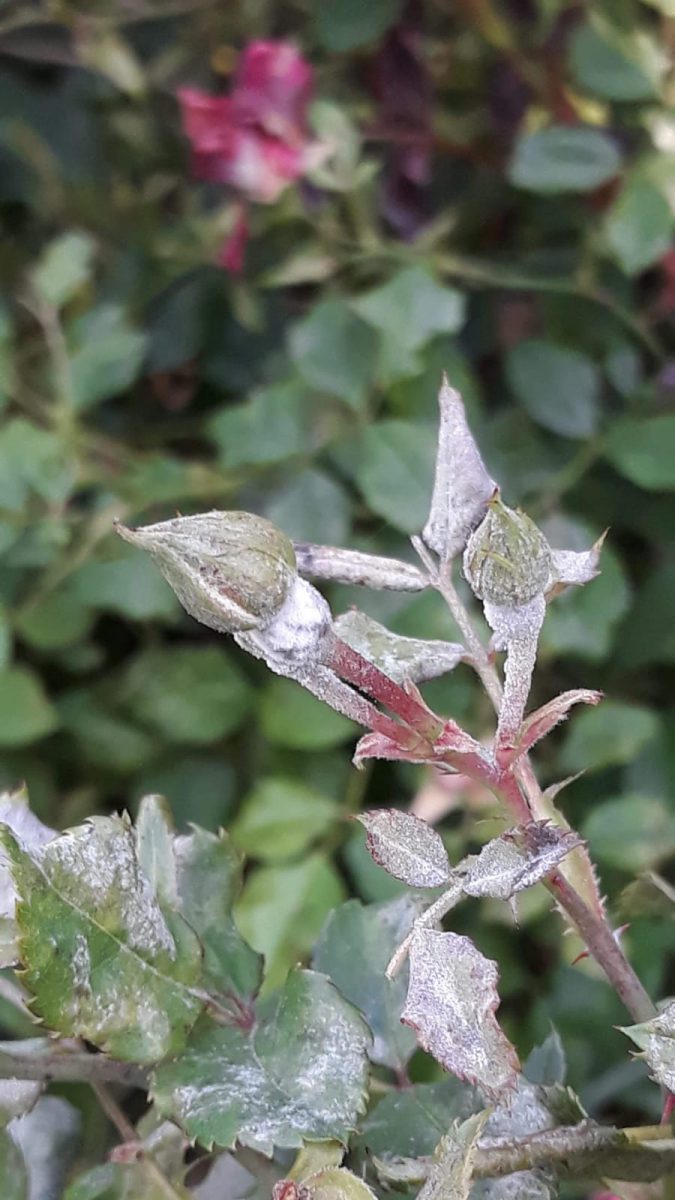
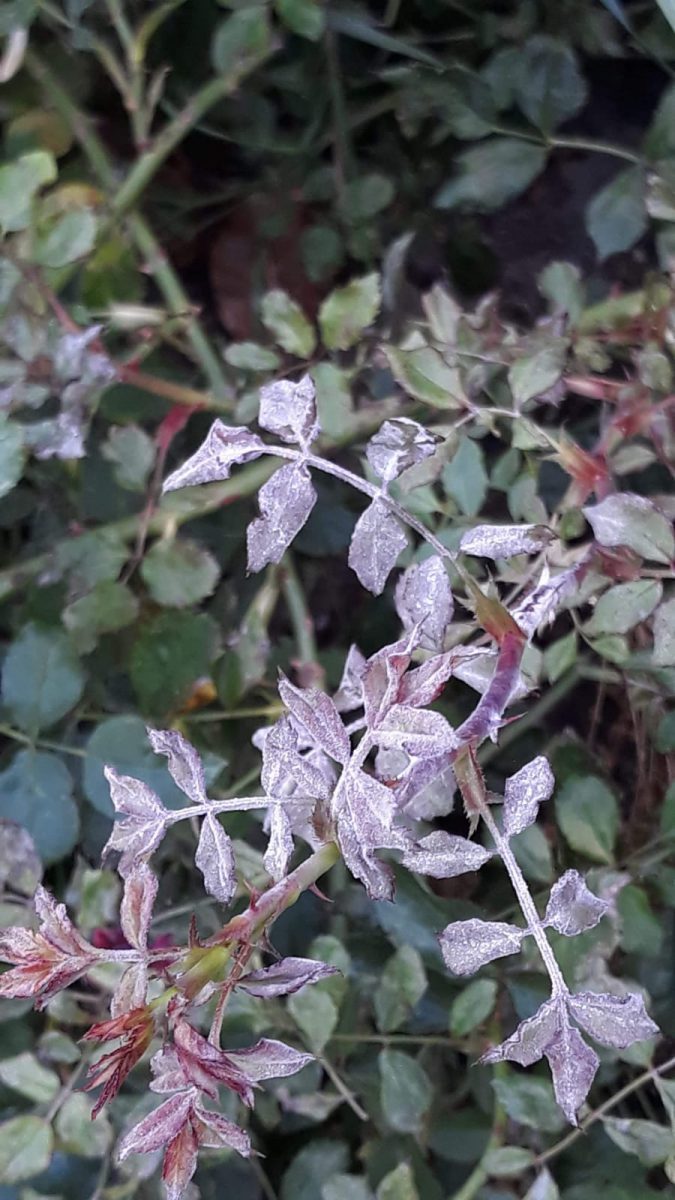
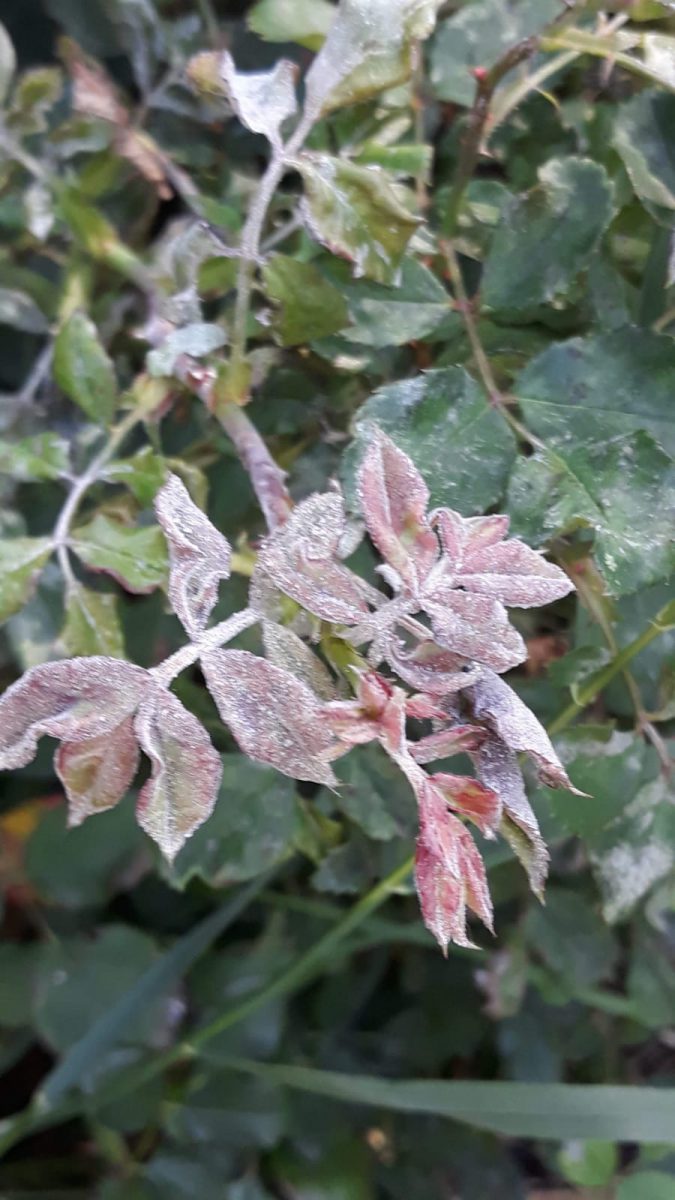



Methods of prevention and control:
- applying specific cuts to keep the bush airy;
- cutting and burning the attacked shoots;
- planting resistant varieties;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
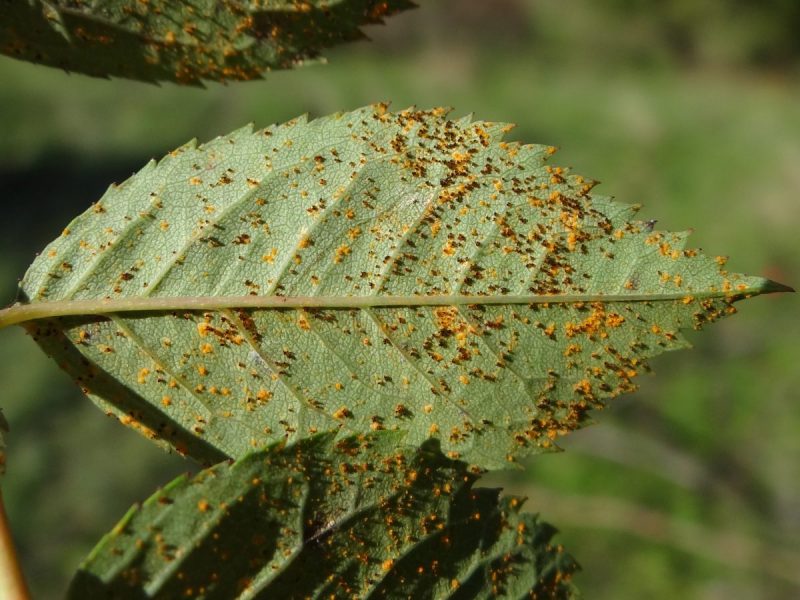
Rose rust caused by the fungus Phragmidium mucronatum. This mycosis can cause symptoms on all the aerial organs of the plant. The first signs are visible at the end of May through the appearance of some discoloration spots on the top side of the leaves. On the underside, groups of yellow spores appear. Towards autumn, the groups of spores change color and become blackish. In case of a strong attack, the plants can lose their foliage.
Methods of prevention and control:
- chemical treatments with fungicides with active substances such as: diphenoconazole, propiconazole, tebucunazole, penconazole;
- planting resistant varieties;
- cutting and destroying severely affected parts.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
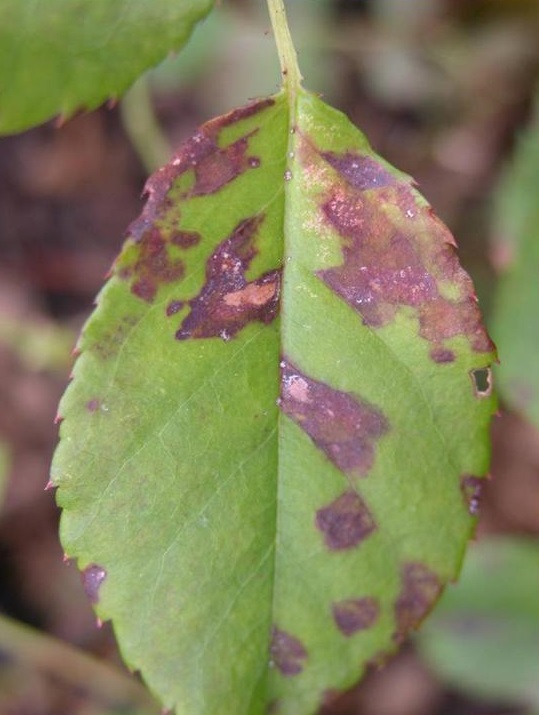
Rose black spot caused by the fungus Diplocarpon rosae. The disease manifests on the leaves of rose plants through the appearance of black, circular spots, on the topside of the leaves. The disease evolves and the spots increase in size. Sensitive varieties are severely affected. The attacked tissues turn brown and finally dry out. The capacity of photosynthesis is reduced and the bushes produce fewer flowers.
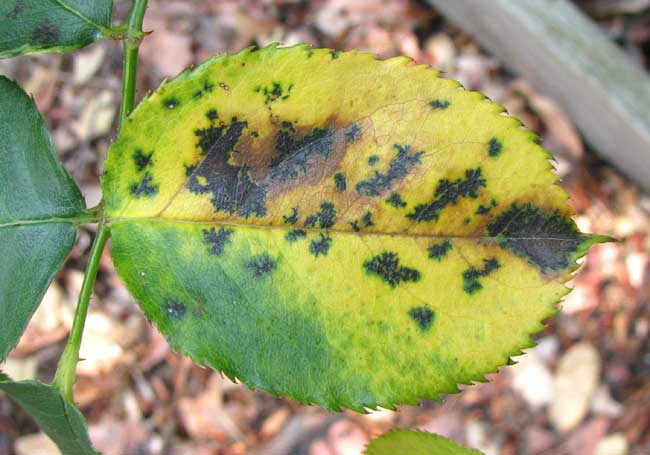
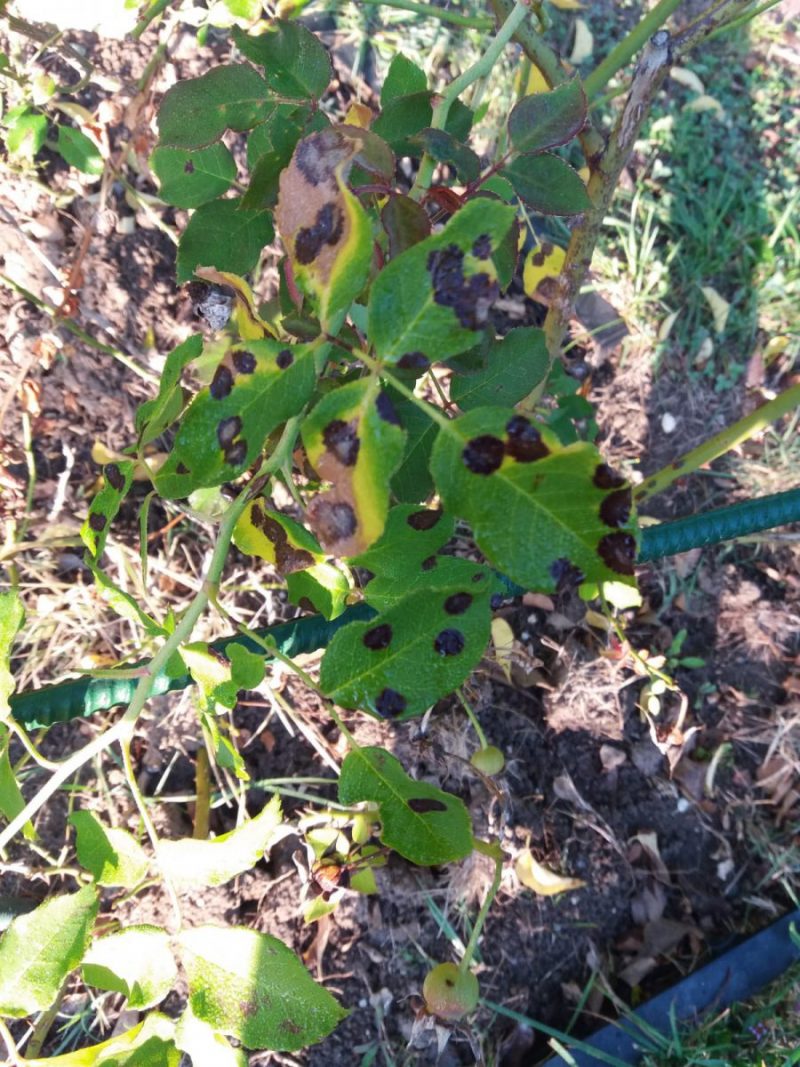



Prevention and control measures:
- cultivation of resistant varieties;
- general hygiene;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Downy mildew caused by the fungus Peronospora sparsa. This mycosis appears in conditions of high atmospheric humidity. Diffuse reddish spots appear on the topside of the leaves. The disease evolves, the spots turn yellow, and a whitish fuzz appears on the underside of the leaves. The attacked tissues no longer develop normally and in the end the whole leaf dries. The capacity for photosynthesis is reduced and the plants produce fewer flowers.
Prevention and control measures:
- performing cuts to keep the bush airy;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Gray mold caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea. The symptoms manifest on all the aerial organs of the rose plants. The most dangerous form of attack is the one on the leaves, flower buds and flowers. The attacked organs turn brown and are gradually covered by the fructification of the fungus that has the appearance of a mold.
Prevention and control measures:
- cutting and destroying severely affected parts of the plant;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The main roses pests
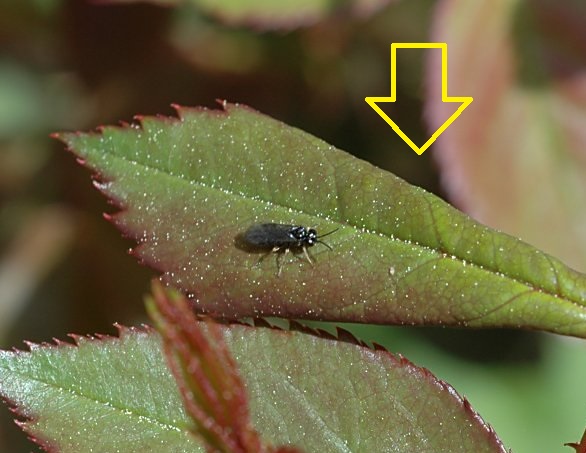
Aphids are polyphagous species that migrate from one plant to another or from one species to another. They develop on spontaneous flora and then move on to cultivated species. They can be found in the form of colonies on the underside of leaves, flowers or inflorescences, and young shoots. Insects sting and suck the intracellular fluid, causing stress to the plant. In case of a severe attack, it determines the decrease of the plant’s resistance to diseases.
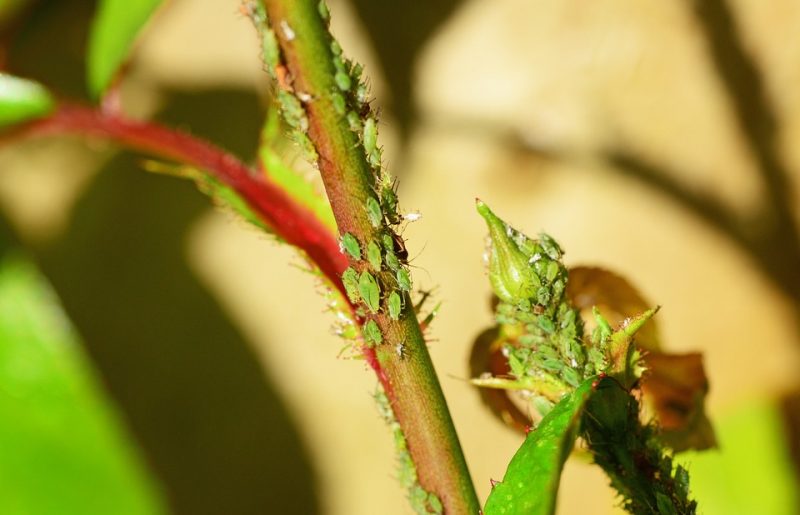
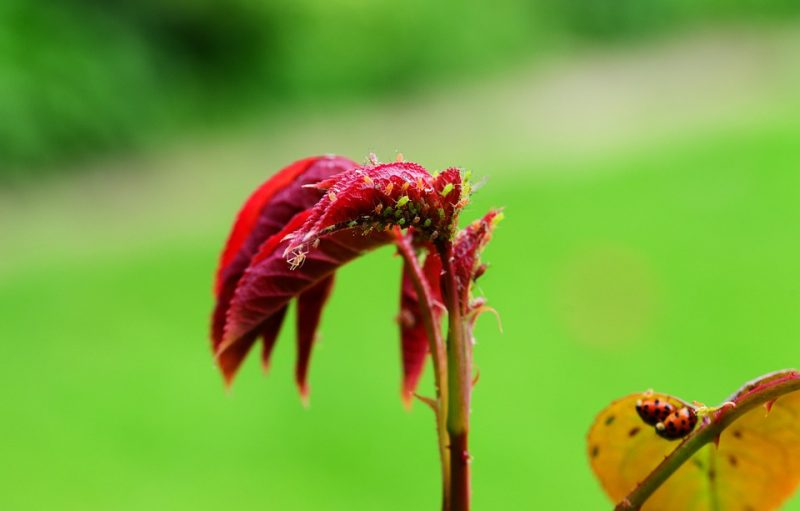
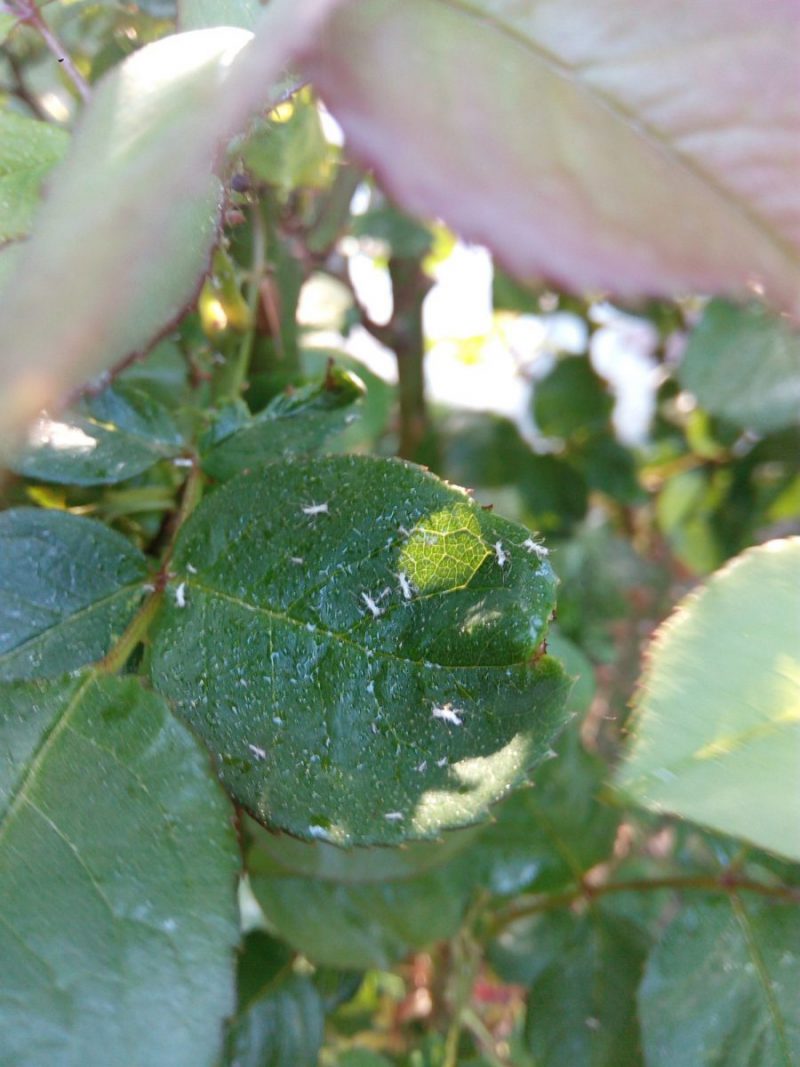




Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
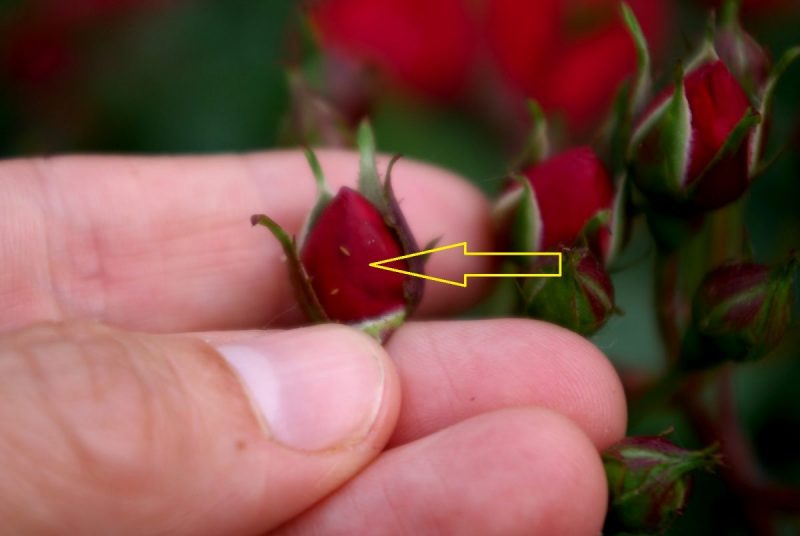
Thrips are small insects, difficult to see with the naked eye, which attack a large number of cultivated plants or fruit trees. They colonize the top of the plants, the flowers, the leaves, causing the falling of the flowers and stagnation of the plants.
Control methods:
- the use of traps with attractants;
- specific insecticide treatments;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
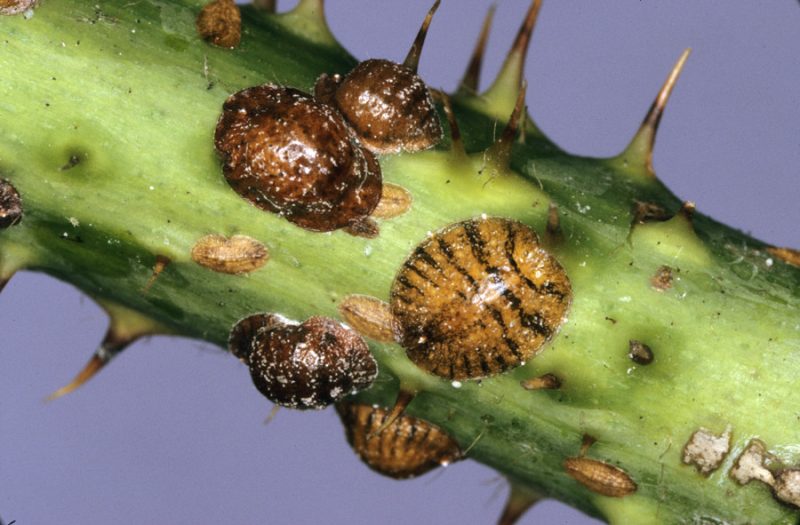
The San Jose scale (Quadraspidiorus perniciosus). It is a polyphagous species that attacks over 200 species of plants. It produces 1-3 generations per year and it overwinters in the larval stage on the bark of the infested species. The females and larvae spread to all organs of the affected plants, feeding on the intracellular fluid of the host plants. In case of a massive attack, the shields that protect the body of the insects overlap and suffocate the plants. They stagnate and after 2-3 years they dry out.
Control methods:
- application of specific treatments during the dormancy period and chemical treatments with specific insecticides during the vegetative growth period;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
- in order to favor the penetration of the insecticide through the wax shield, it is recommended to add an adjuvant to the treatment solution;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
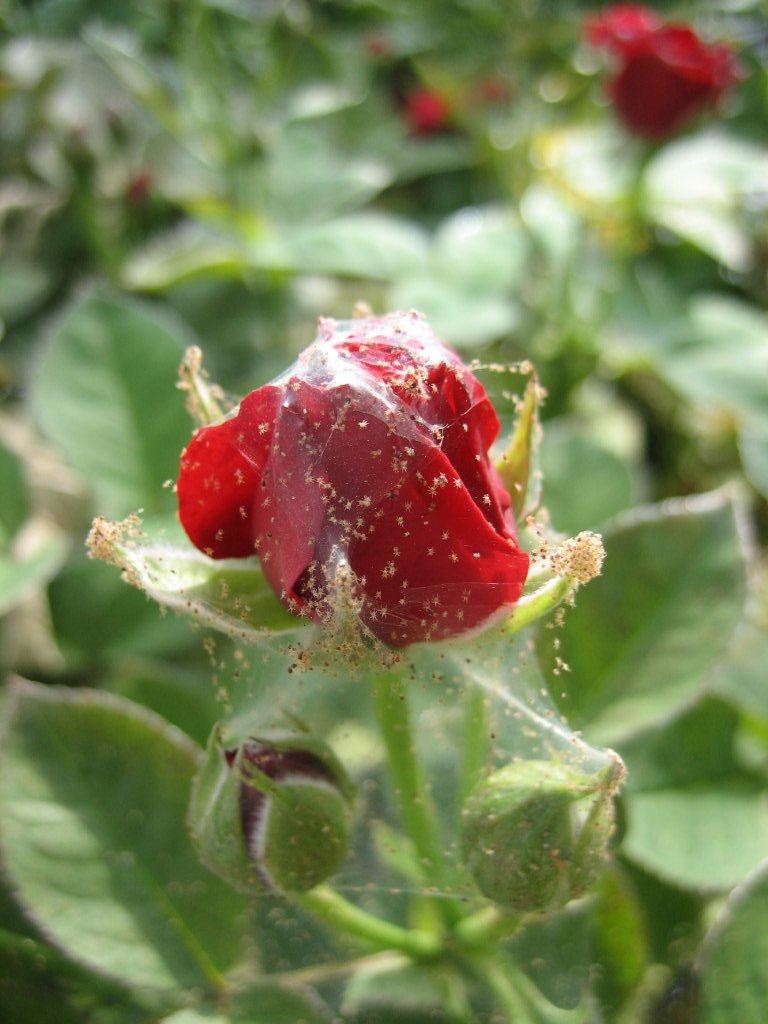
Mites are very small spiders that cause damage to many plant species in protected areas or in fields. The first attacks can occur as early as spring, but significant damage to roses occurs in summer when temperatures are high. They can develop 7-8 generations per year and overwinter as an egg or adult. The spider mites are usually located on the underside of leaves where they feed by stinging the tissues and sucking the intracellular fluid. The first symptoms are visible on the topside of the leaves, which have small, chlorotic spots that turn yellow. After intense feeding, the points merge, the leaves acquire a whitish appearance, then turn brown. On the attacked leaves there is a fine web, in the network of which there are individuals in all stages of development. In addition to leaves, these insects cause damage to flowers.
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with specific products;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
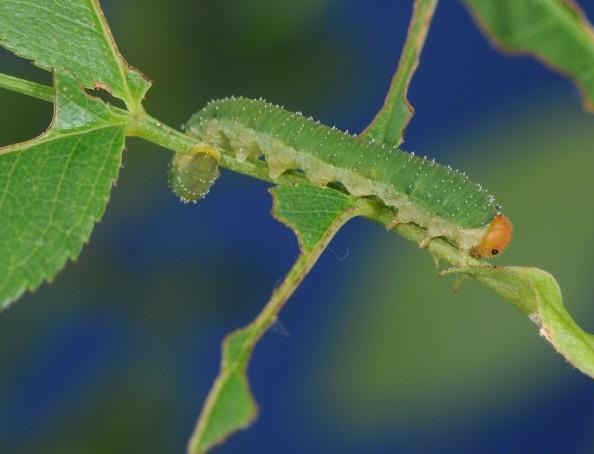
The curled rose sawfly (Allantus cinctus) develops 1-2 generations per year and overwinters as a pupa in the ground. Adults emerge between April and May and feed on nectar and pollen. Females lay eggs on the underside of the leaves, and the larvae hatch after a few weeks. They destroy the epidermis of the leaves, leaving only the ribs.
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with specific insecticides;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Leaf-rolling rose sawfly (Blennocampa pusilla). The larvae of this species are greenish in color. They have relatively large dimensions that can reach one cm in length. Following the attack, the rose leaves curl up towards the underside. The capacity of photosynthesis is reduced, and the shrubs produce a smaller amount of leaves.
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with specific insecticides;
- cutting and burning the affected leaves;
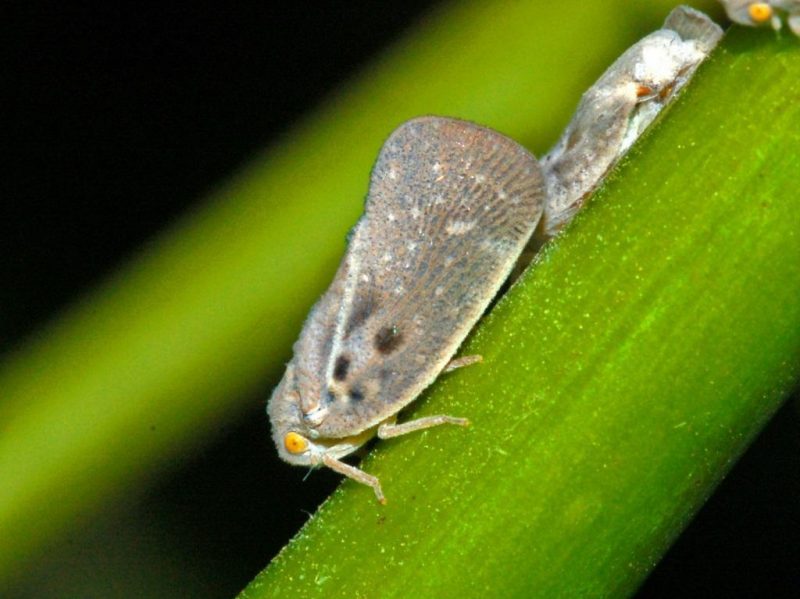
The citrus flatid planthopper (Metcalfa pruinosa). It is a polyphagous species that attacks grapevines, trees, ornamental shrubs and fruit trees. It develops one generation per year and overwinters in the egg stage in the branches of the attacked plants. Adults and larvae feed on the intracellular fluid of the attacked plants, preventing them from growing and spreading numerous viruses. Combating this species is very difficult due to the layer of wax that covers the body of the insects. Because of this layer of wax, it can be easily confused with the woolly apple aphid (Erisoma lanigerum).
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with alternating insecticides from different classes;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
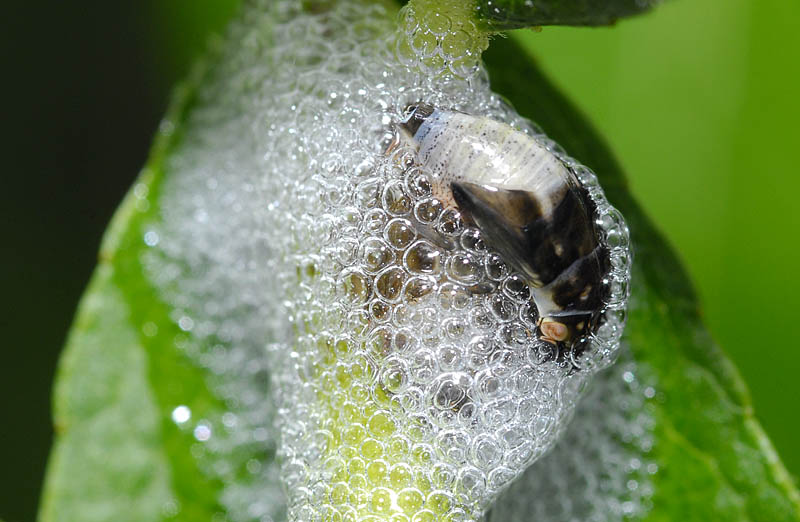
The meadow froghopper (Philaenus spumarius). The insects colonize the plants and feed on intracellular fluid. The nymphs secrete a substance that looks like a foam that protects the larvae during development. Following the attack, the leaves remain small and the plant does not grow normally.
Control methods:
- chemical treatments with broad spectrum insecticides;
Nematodes. They overwinter as adults inside the affected plants and in the soil. They migrate with the help of water from the soil. They live inside the infested plants and feed on intracellular fluid. Following the attack, the roots are deformed and the growth of young leaves is reduced. The attacked flowers remain undeveloped or are even deformed.
Control methods:
- cultivation of resistant varieties;
- the use of healthy planting material;
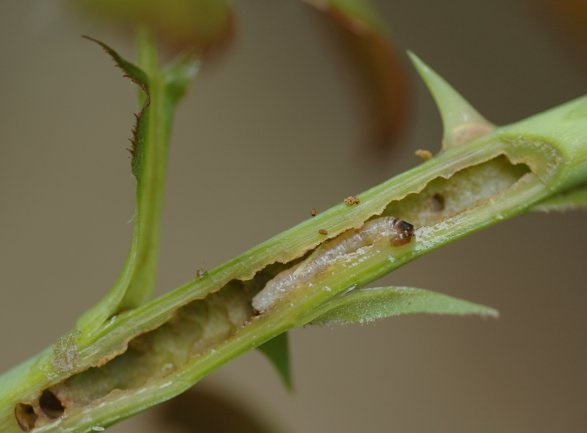
Sawfly (Monophadnus elongatulus). The adults appear in June and feed on the tender tips of the shoots. The females lay eggs in the marrow of the new shoots, close to the top. Above and below the place where she lays the eggs, the female makes a row of perforations, causing the tip to dry. After hatching, the larva makes a tunnel in the stem, descending towards the area between the roots and the stem. The affected stems become weak, break easily and dry out the following year.
Control methods:
- removal and destruction of the affected tops;
- treatments during the vegetative growth period with broad-spectrum insecticides;
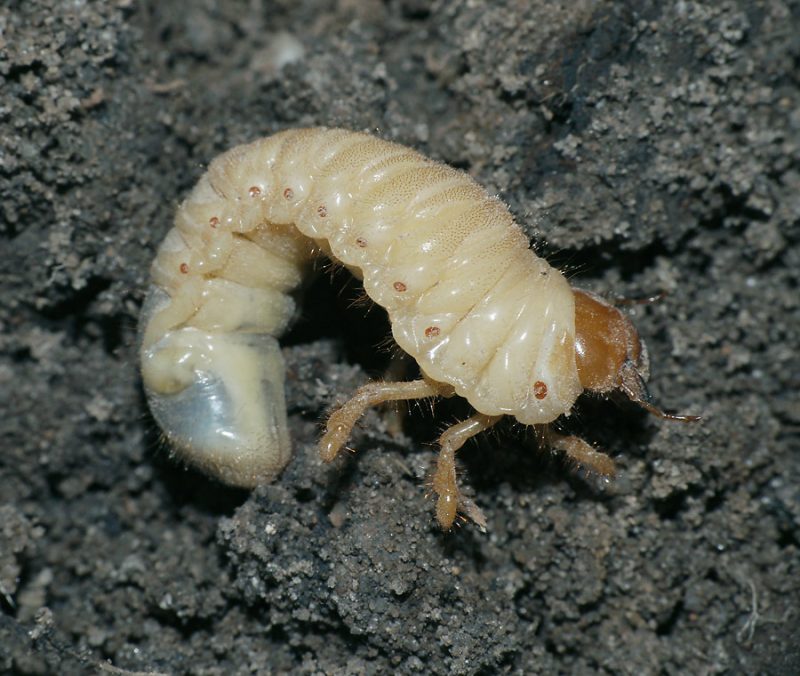
Cockchafer (Melolontha melolontha). This insect is particularly dangerous. It develops a generation once every 3-4 years and overwinters as a larva in the soil. During the developmental period, the larvae feed on the underground parts of various plants, including the rose roots. The attack leads to the withering of the entire bush.
Control methods:
- digging of the soil around the bush;
- application of granular insecticides around the bush;
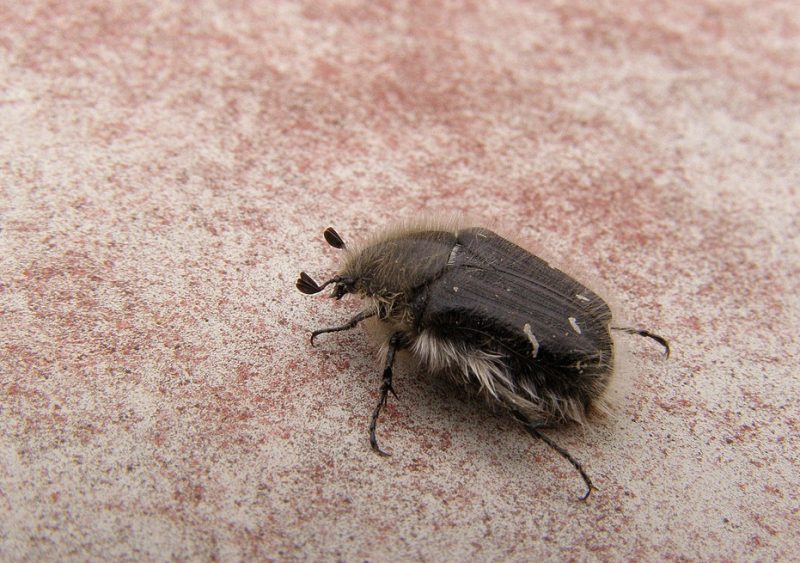
Apple blossom beetle (Epicometis hirta). The adult is 9-12 mm long, matte black, covered with a gray fuzz. It produces only one generation per year and it overwinters as an adult in the soil. Adults feed on floral organs. The larvae are not harmful.
Prevention and control measures:
- chemical treatments with broad-spectrum insecticides;
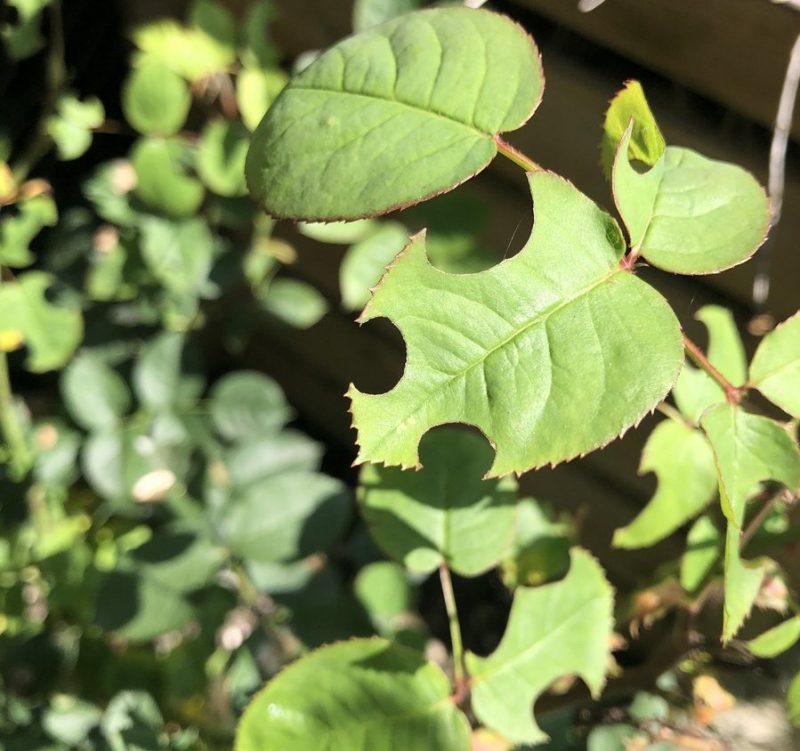
The patchwork leafcutter bee (Megachile centuncularis). It is an insect that forms semicircular incisions in the limb of the rose leaves. Its presence can be signaled starting with May. It is very important to know that the patchwork leafcutter bee does not affect the plants, the damage caused by it being only aesthetic. Because it is a pollinating insect, it is not recommended to control it.