Plant layering – information about vegetative propagation
Vegetative propagation through layering
Like cuttings, layering is a method of vegetative propagation of plants, through which the plants obtained are identical to the mother plant from a genotypical point of view. These methods of propagation are based on the property of the plants to develop roots when their stems or shoots are brought into contact with a substrate. As a result, these methods cannot be applied to all plants but only to certain species.
Layering is an effective alternative for the production of new plants for species whose cuttings develop roots with great difficulty (Camellia, Cordyline, Dracaena, Yucca) or which are difficult to propagate through seeds (magnolia, creeping juniper, vines, and ornamental grapevines). The new plants, called layers, are obtained before their detachment from the mother plant. Rooting occurs faster than in the case of cuttings because the shoot is attached to the mother plant and benefits from its nutrients.
The disadvantage of layering is the small number of plants that can be obtained.
When it is desired to propagate a species through layering, it is recommended that the mother plants be grown specifically for this purpose, be free of diseases, viruses, and pests, properly fertilized, and do not have flower buds or flowers when carrying out the procedure.
The procedure can be carried out starting with spring, before the start of the vegetative growth period, and until the end of June.
Depending on the properties of the plant, the layering can be done naturally or it can be induced.
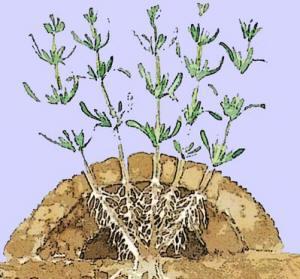
- The natural layering is carried out in the case of species that have thin, flexible stems and shoots, with creeping growth. These plants form a bush at the surface of the soil because their shoots take root easily at the points of contact with the ground. Phlox, Dianthus and Juniperus species are suitable for this type of layering.
- Induced or artificial layering can be done through several methods, depending on the properties of the plant. The development of the roots takes place in 3-6 weeks from the moment the shoots come in contact with a substrate.
Induced layering can be of several types: mound layering, simple layering, serpentine layering, or Chinese layering.
Mound layering
It is used for bushy plants with short stems and buds on the crown or on the stem.
Among the flowering species, it is used for the genus Anthurium ( Anthurium andreanum and Anthurium scherzerianum) and Pandanus weitchii. To apply this method, a mound of soil is made at the base of the plant, which covers part of these buds. Once in contact with the ground, the buds develop shoots with roots at the base that are then detached from the mother plant and planted at the place of cultivation.
In trees and shrubs, cut stems 10-20 cm above the crown in early spring. When the new shoots are about 25 cm high, a mound of soil is made at their base, up to half of their length. The obtained layers have to be cut after 1-2 years, during the vegetative dormancy period. The cut is done leaving a portion of 3-5 cm on the mother plant, on which other shoots develop. The mother plants can no longer be used immediately to obtain layers, but are left to rest for fortification.
Simple layering
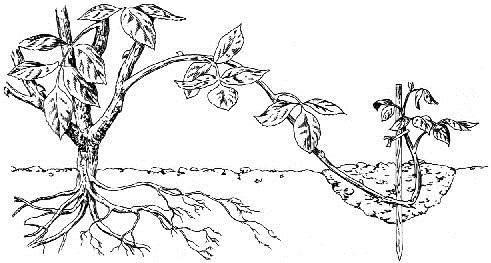
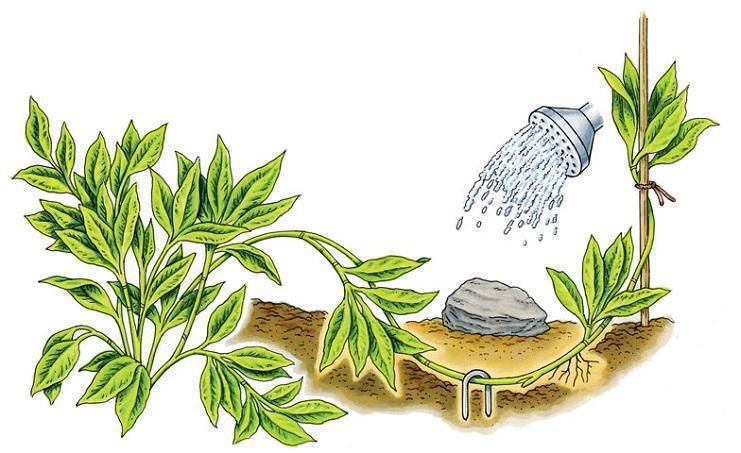
It involves bending the branches and putting them in contact with the substrate. A 10-15 cm deep ditch has to be made in which the shoot is fixed with the help of hooks and the top is supported in a vertical position with a tutor. In autumn, after the vegetative growth period has ended, the layer is separated from the mother plant. It is an effective method of propagating magnolia or maple.
Serpentine layering
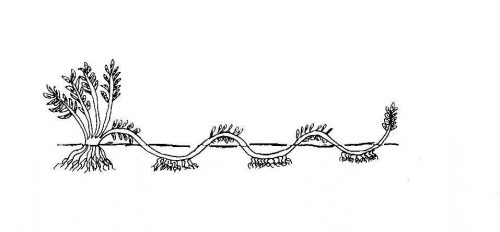
It is practiced on plants with thin, flexible stems, which can be arched and steered to be put in direct contact with the ground at the desired points. Suitable plants are wisteria, ivy, ornamental grapevine, traveler’s joy, Ficus pumila, Philodendron, Pothos, Syngonium. The stems are fixed to the ground with a grip, next to the nodes, in as many points as we want layers to obtain, and as long as the length of the stem allows. After rooting, the layers are detached from the mother plant and planted separately.
Chinese layering
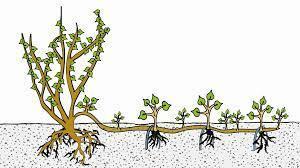
It involves digging a 15-20 cm deep ditch in which the branches to be layered are fixed with the help of hooks. These branches are not covered with soil from the beginning. When the shoots from these branches are 25-30 cm high, the ditch is covered with damp soil. After the roots have developed, the shoots (new layers) are separated from the mother plant and planted separately. The shoots near the crown must be left to be used later for a new layering. The Chinese layering is used for juniper, ash, maple, gooseberry bush, currant, blackberry, hazel, fig, etc.
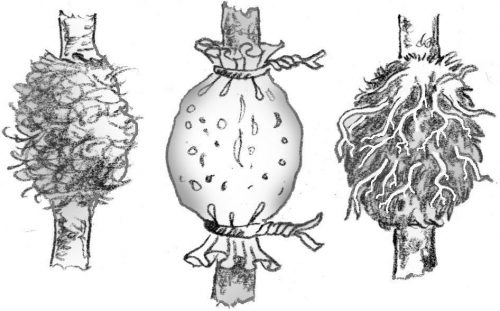
Air layering
It is used for species with thick, tall stems that cannot be bent to the ground, such as Ficus, Leander, Camellia, Cordyline, Croton, Yucca, Schefflera, Dracaena, Magnolia. The method is usually used for specimens that no longer have leaves at the base, having a hollow appearance. In this case, the substrate necessary for the development of the roots is fixed on the stem with the help of a polyethylene sleeve. Fibrous peat or a well-moistened moss can be used as a substrate. The substrate is fixed in the place where the rooting is desired and to ensure its success, circular incisions can be made on the stem and rooting hormones can be used. After root formation, the layer is detached from the mother plant and it is planted separately.