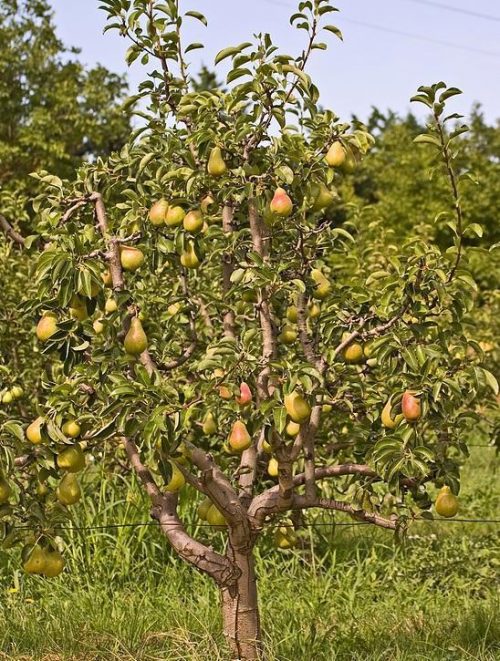
Pear tree, planting, growing and harvesting
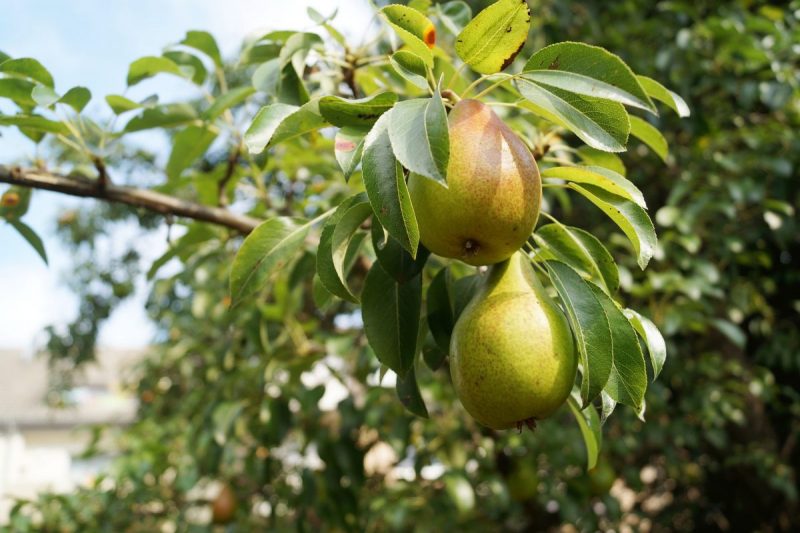

The pear tree (Pyrus commnunis) is a fruit tree native to Asia. The crown has a characteristic shape and can reach 20 m. On the stem and the old branches, the bark exfoliates. The leaves are oval or round, and the petiole is pubescent. The flowers are white and appear at the same time as the leaves. The pear tree is widespread in culture due to its nutrient-rich fruits. These contain water, sugars, tannins, fiber, zinc, copper, iron, calcium, magnesium, and vitamins.
Growing and fruiting particularities
The root system develops according to the rootstock. If the tree has been grafted on quince, the root system will be poorly developed. The growth rate of young trees is much lower than that of apple trees. Young trees need extra support to avoid a crooked trunk. The central axis dominates the whole crown.
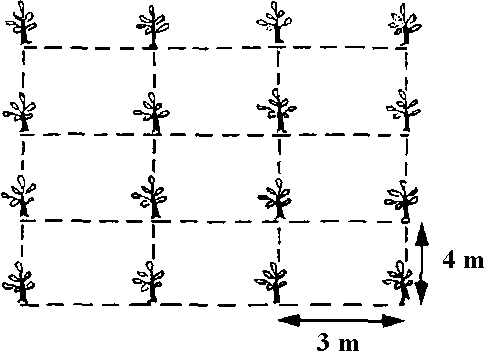
The pear tree reaches larger dimensions than the apple, for this reason, when planting, the appropriate distance between the rows must be ensured to avoid the mutual shading of the trees. The vegetation starts in early spring, about a week before the apple tree. Due to the slow growth rate in the first years, the first yields are low. The pear tree returns to normal after 5-6 years of life. Most cultivated pear varieties are self-sterile (they cannot pollinate on their own). For this reason, it is recommended to plant several varieties in the orchard, including the best pollinators. Planting material should be purchased only from licensed nurseries or research centers.
Climate and soil requirements
The pear tree requires higher temperatures during the growing season than the apple tree. Good results are obtained where average annual temperatures are between 9.5 and 10.5 °C. The optimum temperature range for pear tree growth is between 20 and 35 °C. Some varieties withstand temperatures up to -28 °C in winter. The flower buds are affected by temperatures lower than -3.3 / -5.5 °C, and the flowers already opened withstand temperatures up to -2.2 / -4.4 °C.
The pear tree does not have high requirements for soil moisture, autumn and winter varieties grow well in areas with about 700-900 mm of rainfall/year, and summer varieties require rainfall of up to 600 mm/year. The tree is resistant to excess water in the soil. However, prolonged drought reduces the number of flower buds, and the tree forms small, deformed fruits. Groundwater must be at a depth of more than 2.5 m. The pear tree is light-demanding, and if the trees are shaded, the fruit has poor quality, so orchards with southern exposure are recommended. Prefers deep, loose, and loamy soils with a loamy-clayey texture and a neutral pH.
Soil preparation
The plot on which the orchard will be established must have a southern exposure and the rows must be oriented north-south. This ensures a large amount of light during the day. The soil should be worked at least three months in advance. If the plantation is established on land that has been used as an orchard, the land should be prepared 1-2 years in advance. To restore the soil structure and eliminate the infection outbreaks, the land can be cultivated with perennial grasses. If the land is heavily infested with weeds, you can apply a non-selective herbicide.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The soil can be fertilized with organic fertilizers (manure, compost). Also, it is recommended to scarify the soil so that the roots grow easily. All foreign matter in the soil should be collected and removed from the plot, after which the soil must be well-leveled.
For precise planting, the land can be picketed. Picketing is the process of marking the position of each cherry tree on the ground. Specifically, a stake is inserted into the tree planting site.
Planting
For planting use well-developed, healthy planting material with a well-developed root system. Planting material should be obtained from authorized nurseries. At the time of planting, the trees must be dormant and the soil should not be frozen. Under the right environmental conditions, autumn planting is most recommended. The pear tree planted in autumn will benefit from the water accumulated during rainy periods and from melting snow and will start growing earlier in spring.
To stimulate root development, the roots should be trimmed. The operation is performed to remove the damaged portions and to maintain a healthy root system. Necrotic roots must be completely removed, and the healthy ones must be shortened by 7-8 cm. Trimming must be done only if the cherry saplings have been recently removed from the ground.
After trimming, the roots must be soaked. Mudding means dipping the root into a mixture of yellow soil, fresh manure, and water. The mud layer helps the tree to adapt to the new soil conditions and maintains the moisture around the roots.
Actual planting
In the semi-intensive system, the most commonly used planting distances are 4 meters between rows and 4 meters between trees per row. In the intensive system, the planting distances used are 4 meters between rows and 3 meters between trees per row. If the land has not been worked before planting, the pit should be dug 2-3 months before planting. If the land has been worked properly, the pit should be dug 1-2 days before or even the same day. At the base of the pit, you can introduce a mixture of fertile soil removed from the topside of the pit and well-decomposed manure. Insert the tree into the pit so that the root stays on the fertile layer at the base.
The tree should be planted so that the grafting point is 10-15 cm above the ground. When planting, the roots must be in close contact with the soil. After planting, apply fertilizers by incorporating and watering the soil abundantly. Repeat watering whenever needed. Insert a stake next to the sapling, for additional support. After planting, the saplings should be shortened to a height of 80 cm. The sapling can be covered with rodent protection materials.
Care works
In the spring, provide the necessary amount of water. In the case of young pear orchards, irrigation is mandatory. Around the trees, the soil should be dug superficially and covered with plant debris (mulch). Mulching maintains a good phytosanitary condition, prevents the development of weeds, conserves water in the soil, and reduces the number of maintenance works.
In the pear tree case, pruning must be carried out every year.
Pruning makes the difference between a productive tree and a problem tree. Essentially, pruning must ensure:
- balance between growth and fruition;
- light penetration into the crown;
- crown lateral branching;
- production quality.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
In the first year, in spring, the tree can be pruned to a height of 80 cm. Once the tree has started to grow, all the leaves up to a height of 50 cm should be removed. From the upper part of the tree, pick 3-4 evenly twigs to form the first level of the crown. The rest of the twigs must be removed from the plant. In the second year of vegetation, the selected twigs must be shortened to 50 cm, above an outward-facing bud.
In the third year, in early spring, the extension twigs of the main pear branches must be shortened to 50-60 cm. The cuts should be made above an outward-facing bud. On the central axis choose 3-4 twigs arranged evenly on the tree, to form a new level. Remove competing branches and branches that shade each other. The remaining branches on the axis should be shortened to 10-15 cm to bear fruit. In summer, remove water sprouts, competing branches, and those on the upper part of the main branches. In the fourth year, limit the tree height to 2.5 m, with a cut above an outward-facing branch. The growing bud at the top of the central axis is dominant. Because of this, the pear tree grows much taller. After pruning, the tree must be aired and sunlight must reach all branches.
Pruning in the following years begins by removing weak, dry, broken, or diseased branches.
All twigs inside the crown, which have a luxuriant growth must be removed. New branches that are longer than 60 cm must be shortened to about 70% of their original length. The fruiting branches are short and have a single bud at the top. From this bud will form complex fruit formations. All cuts should be made at a 45-degree angle. This way, the water will drain easily from the wound. If by cutting, wounds are larger than 2 cm, they must be covered with tree wound sealer.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Several operations can be carried out to control pear tree growth and fruiting:
- Branch training: represents the change of natural position of the branches, towards the vertical. This causes the branch to grow and strengthen. This operation should carried out mainly in the mature phase of the trees. In this phase, the vegetative growth ceases and this operation leads to crown rejuvenation.
- Branch tying down: it consists in changing the position of the branches, towards the horizontal. This causes the buds on the branch to differentiate and aerates the crown. Branches can be tied down below the horizontal to obtain abundant fruiting. This operation is practiced in the young stage of the trees when vegetative growth is predominant.
- Branch arching: through this change of position, the basal part remains ascending, and the terminal part is inclined below the horizontal (descent). This operation stops or slows down the growth in length of the branch and promotes bud growth. Trees that have been arched begin to bear fruit 2-3 years earlier.
- Transverse incision: represents the disruption of the vessels by a fine cut with a sharp blade. The cut must be made above a bud;
- Longitudinal incision: represents a fine cut along the length of the trunk. This operation helps to increase the thickness of the trunk;
- Twisting: consists of twisting a branch or twig. This operation stimulates fruiting;
- Branch breaking: it is practiced in the case of branches that have an inappropriate orientation. Fruiting occurs quickly on broken branches.
Weed control
The interval between rows must be kept clean. Weeds can be cut with a weed cutter to add organic matter to the soil or removed chemically, with herbicides approved for pear trees. Herbicides should be applied with care so that the solution vapors do not touch the leaves of the trees. During the first three years after planting do not use herbicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Protecting trees from frost
When low temperatures are announced, in the orchard, you can burn easily burning materials (gathered in piles), which produces a large amount of smoke (rubber, straw, manure, tar, peat, etc.). Thus, the smoke layer that forms above the orchard does not allow heat to be released from the soil and thus maintains a higher temperature at the trunk/tree crown level. It is important to keep the fire on throughout the night, especially before sunrise, when temperatures drop sharply. This operation can protect the trees from temperatures down to -3 °C.
Fertilization
The pear tree reacts well to organic fertilizers (manure, granular fertilizers). Besides basic fertilization, you can also apply foliar fertilizers periodically during the growing season. Fertilization (dosage, ratio of elements) should be done only after a chemical analysis of the soil.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Pollination of pear orchards is a problem.
Pear flower nectar is low in sugars and bees are not attracted to it. Also, pear trees bloom in a cold, wet period. To solve this problem, place several hives in the orchard. For one hectare of the orchard, use 3-4 hives.
Irrigation
The pear tree has lower water requirements than the apple tree, and if exposed to high humidity (especially in the second half of the growing season), it can easily develop specific diseases. Because the pear root system develops to depths of about 50 m, the most suitable method of irrigation is by drip.
Pests and disease control
The phytosanitary condition of the pear plantation is very important. Carrying out phytosanitary treatments according to a specific schedule can significantly reduce the occurrence of diseases and pests.
At the same time, keep the orchard clean. Pick up fallen leaves or branches and cover the trees with special solutions.
To destroy outbreaks of infection in the orchard, apply treatments during the dormant period. Treatments should be applied in autumn/winter when the temperature is above 5 °C.
Against diseases, the first treatment (after leaf fall) should be done with copper-based products. The second spraying with copper-based products must be done in spring, at bud break. The solution should be sprayed all over the tree, from the base of the tree to the branches. These treatments need to be applied on days without rainfall, with temperatures above 6-7° C, so the solution does not freeze on the trees. 7-10 days after applying the copper treatments, apply a horticultural oil treatment, which acts against pests that may overwinter in the bark of the tree.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Harvesting
Due to the high perishability, summer and autumn pears are harvested 7-10 days before consumption maturity, when they have reached the size and color characteristic of the variety. If they are harvested at maturity, the pulp is soft and the fruit cannot be stored or handled.
Winter pears are harvested as late as possible to accumulate as many carbohydrates and flavors as possible. The fruits can be stored for 1-2 months in dark storage, at temperatures of 4-5 °C.