Lettuce, treatments against pests and diseases

Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) is a vegetable plant of the Compositae family. It is grown in the field and protected areas, especially for its leaves, which are used to prepare salads. This plant is also very suitable for hydroponic cultivation. Currently, there is a wide variety of varieties and hybrids on the market. The lettuce crops can be affected by pests and diseases, against which it’s important to apply the right treatments.
The main diseases of lettuce
Viruses
Lettuce mosaic virus
On attacked plants, discoloration spots appear on the tissues between the veins. These give the plant a mosaic appearance. In case of a severe attack, these symptoms may be accompanied by swelling or even burns. The plants remain small after the attack. The virus is transmitted by different species of aphids and also through infected seeds.
Prevention and control measures:
- using healthy seeds;
- weed control to limit the aphid population;
- using specific insecticides to control the aphid population.
Mycosis
Downy mildew (Bremia lactucae)
The disease appears on the basal leaves near the soil. Large, glassy-looking spots appear on the leaves and a fine, whitish fuzz appears on the underside, representing the fungus’ fructifications. In case of a severe attack, the disease can cause the whole plant to rot. Disease occurrence is favored by temperatures between 15 and 17℃ and high atmospheric humidity. The fungus is transmitted by spores which are carried by vectors (water, air, animals, people, tools, etc.). The disease can also occur in the seedling stage.
Prevention and control measures:
- destroying plant debris after harvest;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- optimum planting density and carrying out plant thinning;
- weed control to promote air circulation;
- preventive lettuce fungicide treatments that can be applied in the seedling phase and at times when the disease is most likely to appear.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Powdery mildew (Erysiphe cichoracearum)
A very fine white blotch appears on the upper part of the leaves, and as the disease progresses, the blotch becomes grey and dusty. The attacked leaves become discolored and lose their gloss. Eventually, the tissues under the mycelial layer dry out and detach from the plant. The fungus attacks the plant in conditions of high humidity and low insolation (“cloudy”). The fungus is transmitted by spores which are carried by vectors (water, air, animals, people, tools, etc.). The disease survives during winter on plant debris left on the ground.
Prevention and control measures:
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- destroying plant debris after harvest;
- growing resistant varieties;
- lettuce treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
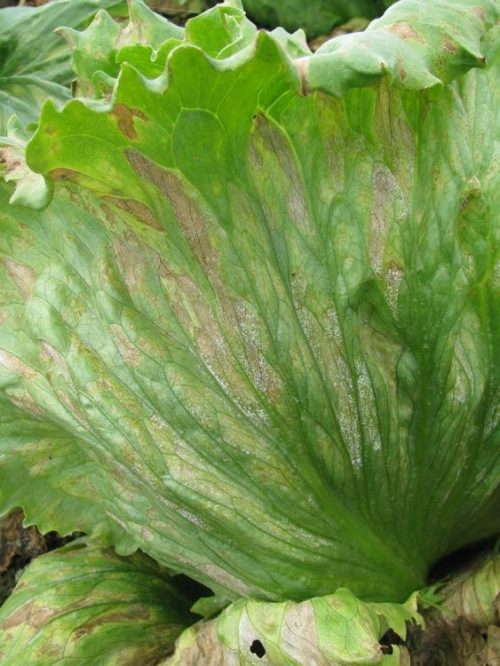
Septoria leaf spot (Septoria lactucae)
Yellow spots appear on the basal leaves, which turn brown. As the disease progresses, a whitish mycelium appears in the middle of the spots, accompanied by a multitude of small black dots. Septoria can attack all organs of the plant. The disease is transmitted by spores carried by vectors (water, air, animals, people, tools, etc.). The disease is transmitted from one year to the next via seeds or infected plant debris left on the ground.
Prevention and control measures:
- destroying plant debris after harvest;
- using certified, disease-free seeds;
- specific fungicide lettuce treatments for prevention and treatment
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
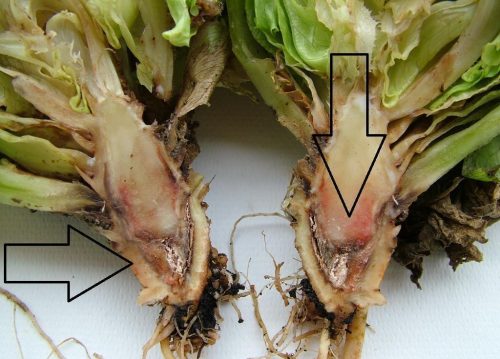
Fusarium wilt (Fusarium spp.)
Initial symptoms are wilting of the lower leaves, often on one side of the plant. Attacked leaves turn brown and fall off, eventually wilting the whole plant. If a section is made through the root, we can see that the plant vessels are browning. The fungus penetrates the root and blocks the plant’s vessels.
Prevention and control measures:
- using healthy and certified seeds;
- removing and destroying diseased plants from the crop;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
Damping-off (Pythium spp.)
A brownish patch appears on the young plant’s crown area, and shortly afterwards the seedlings show symptoms of wilting.
Prevention and control measures:
- avoiding excess watering;
- regular airing of seedlings, to adjust air humidity;
- using disease and pest-free substrate or disinfecting the substrate before sowing;
- using certified seeds;
- preventive and curative treatments.
White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)
Attacked plants show symptoms of yellowing and wilting. The attack evolves on the lower part of the stem, where white or light yellow areas appear, which later turn brown. In the affected areas the fungus sclerotia develops, which ensures year-to-year transmission.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- removing affected plants from the crop;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- balanced fertilization;
- disinfecting seeds and substrate for hotbed;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
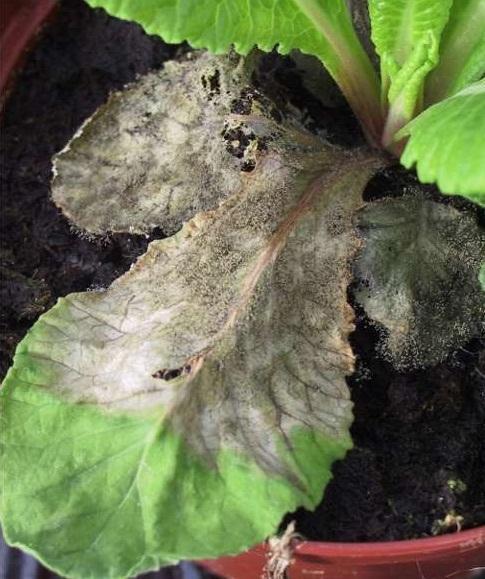
Gray mold (Botrytis cinerea)
The disease appears in conditions of high humidity and cloudy weather (fog). The attacked areas become discolored and brown and as the disease progresses, a grayish mold appears on the affected areas, representing the fungus’ fructifications.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- rational fertilization;
- regular airing of the protected areas;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Lettuce anthracnose (Microdochium panattonianum)
Wet, brown spots appear on the outer leaves. The disease evolves, and the spots increase and become circular, bordered by a brown halo. The affected tissues sink but do not detach from the plant. The disease deforms the plant and in case of severe attack, the leaves become inedible.
Prevention and control measures:
- correct crop rotation;
- avoiding sprinkler irrigation;
- growing resistant varieties;
- treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
The main pests of lettuce
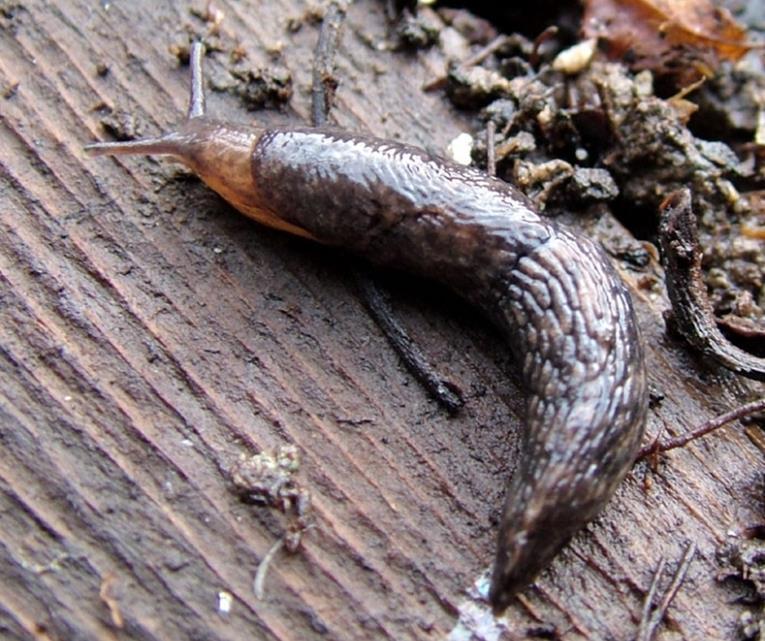
Slug
It is a polyphagous species, which attacks many vegetables, flowers, vines, etc. It causes great damage to vegetable crops, perforating the leaves, and digging deep cavities.
Prevention and control measures:
- specific molluscicide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Aphids
They are polyphagous species that migrate from one plant to another or from one species to another. Aphids grow on spontaneous flora and then move on to cultivated species. They are found as colonies on the underside of leaves, on flowers, on inflorescences, and on young shoots. Insects sting and suck the plant sap, resulting in plant stagnation and yellowing.
Prevention and control measures:
- weed control;
- specific insecticide treatments;
- using sticky traps.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum)
The pest thrives in greenhouse conditions all year round, and in the field only in summer. In the greenhouse, it can develop 3-6 generations when conditions are favorable. Adults and larvae colonize leaves, often also the shoots. Following the attack, leaves turn yellow, dry out, and fall off.
Prevention and control measures:
- destroying plant debris after the crop is harvested;
- disinsecting greenhouses and polytunnels before setting up a new crop;
- specific lettuce insecticide treatments;
- using sticky traps.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
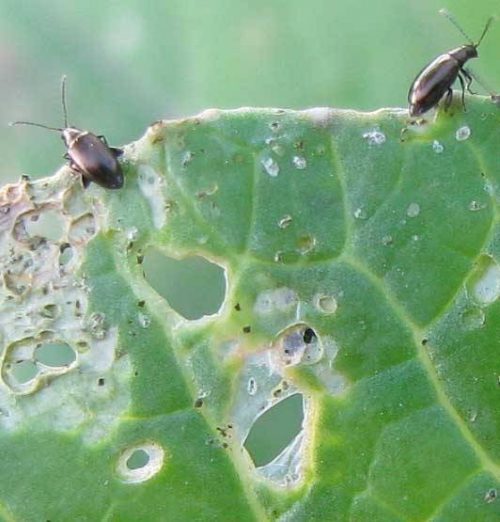
Flea beetle
The adults appear in early spring, and after feeding they lay their eggs in the soil, next to the cabbage, cauliflower, kale, and lettuce plants. Adults attack the leaves and gnaw the tissues, leaving the leaves with a pitted appearance.
Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
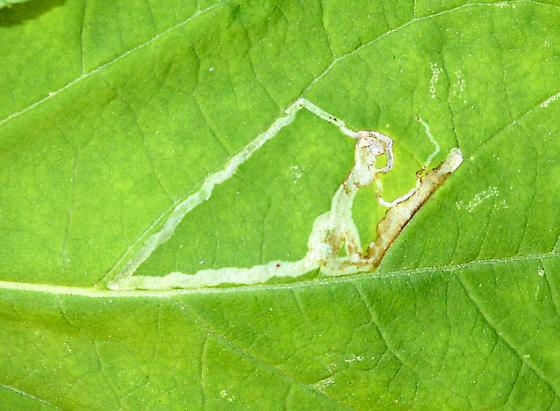
Leafminer (Liriomyza spp.)
It is a polyphagous species that attacks almost all vegetable species. The larvae gnaw in the leaves, forming mine galleries, but the attack does not cause significant damage in most cases.
Control methods:
- specific insecticide treatments.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store