Garlic, treatments against pests and diseases

Garlic (Allium sativum) is a widespread herbaceous plant belonging to the Liliaceae family. This plant is widely used as a food and condiment, as well as in the pharmaceutical industry, due to its properties. The most widely used part of garlic is the bulb, made up of several bulbils, popularly called “garlic cloves”. Garlic was introduced into cultivation 6000 years ago and is now cultivated in all parts of the world. Garlic crops can be affected by pests and diseases, against which it’s important to apply the right treatments.
MAIN DISEASES OF GARLIC
Viruses
Leek yellow stripe virus
Attacked plants have slowed growth and signs of discoloration. Leaves droop and show yellow streaks. In case of a severe attack, the whole plant turns yellow. In vegetation, the virus is spread by aphids, and from one year to the next, disease transmission is ensured by infected planting material.
Prevention and control measures:
- the planting material must be healthy;
- growing resistant varieties;
- insecticide treatments to keep aphid populations under control;
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Bacteriosis
Soft rot disease (Erwinia carotovora pv. carotovora)
The disease makes its appearance at the end of vegetation. The stems of attacked plants develop weakly while a wet rot appears at their base. The bulbs change color and soften. The bacterial attack also continues in the warehouse, where the bulbs rot and emit an unpleasant smell.
Prevention and control measures:
- balanced fertilization;
- correct rotation (garlic can be planted on the same land after a minimum of 3-4 years).
Mycosis
Downy mildew (Peronospora destructor)
The disease attacks bulbs, flower stalks, and leaves. The first symptoms appear on the leaves as elongated, light green to yellowish spots on which a greyish-purple fuzz forms. The attacked tissues soften and cause the leaves to dry out and fall to the ground. The optimal conditions for the disease are high air humidity for at least 10 hours and low temperatures around 12℃.
Prevention and control measures:
- cultural hygiene;
- balanced fertilization;
- correct rotation (garlic can be planted on the same land after a minimum of 3-4 years);
- garlic treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Purple blotch (Alternaria porri)
The disease manifests on all organs of the plant as small, whitish spots surrounded by a yellow ring, which later turns brown. In case of severe attack, the fungus also attacks the bulbs. The disease can also continue its activity in warehouses if the spaces are poorly ventilated and humidity and temperatures are high. The fungus spreads by spores carried by water and wind droplets, and in winter it lives on plant debris on the soil surface.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- correct crop rotation (garlic can return to the same land after a minimum of 4 years);
- growing resistant varieties;
- garlic treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
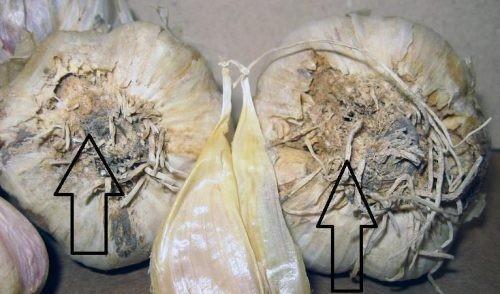
Neck rot (Botrytis allii)
Whitish, circular spots appear on the leaves and bulbs, where the tissue sinks. In conditions of high humidity, a greyish fuzz appears on these spots, where the fungus sclerotia develops. The fungus is transmitted from one year to the next through the sclerotia and infested seeds.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- correct crop rotation (garlic can return to the same field after at least 4 years);
- rational irrigation;
- garlic treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
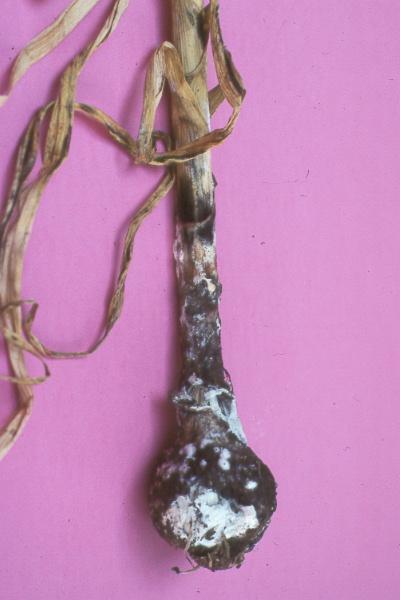
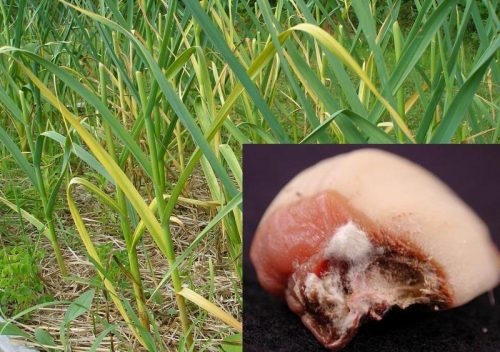
White rot of onion and garlic (Stromatinia cepivora)
It is one of the most damaging diseases of garlic, occurring in springs with heavy rainfall. The attack manifests by yellowing of the outer leaves at first, followed by the younger ones. Attacked plants stagnate in growth. When the disease progresses, the stem rots in the crown area. Symptoms can be seen most clearly on the underside of the plant, where white rot forms, on which small black sclerotia form. These transmit the disease from one year to the next.
Prevention and control measures:
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvest;
- correct crop rotation (garlic can return to the same land after a minimum of 4 years);
- rational irrigation;
- removing diseased plants from the crop;
- garlic treatments with specific fungicides.
Recommended products
-
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store -
You can find products on a different store
Change Store
Rust (Puccinia allii)
Initial symptoms consist of small, irregularly shaped, light brown or white spots on the leaves. Later these spots enlarge and develop the typical disease pustules, which are dark orange. Severe attack leads to leaf drying and plant wilting.
Prevention and control measures:
- removing diseased plants from crops;
- correct crop rotation (garlic can be planted on the same land after at least 3-4 years)
- growing resistant varieties;
- balanced fertilisation;
- gathering and destroying plant debris after harvesting;
- chemical treatments with specific fungicides.
Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae)
The disease settles only on the underground organs of the plant and is very difficult to detect. The leaves show a slight yellowing of the upper part while the affected roots turn pink and rot. Diseased bulbs show a light softening in the basal part, but in high humidity conditions, a whitish fuzz appears on the infected areas. Fusarium fungi are present in the soil in most fields and it is recommended to plant resistant or tolerant planting materials.
Prevention and control measures:
- growing resistant varieties;
- using healthy planting material.
Dry rot (Helminthosporium allii)
This disease causes black spots to appear on the bulb tunics, reducing the commercial appearance of the crop. Bulbils are not affected.
THE MAIN PESTS OF GARLIC
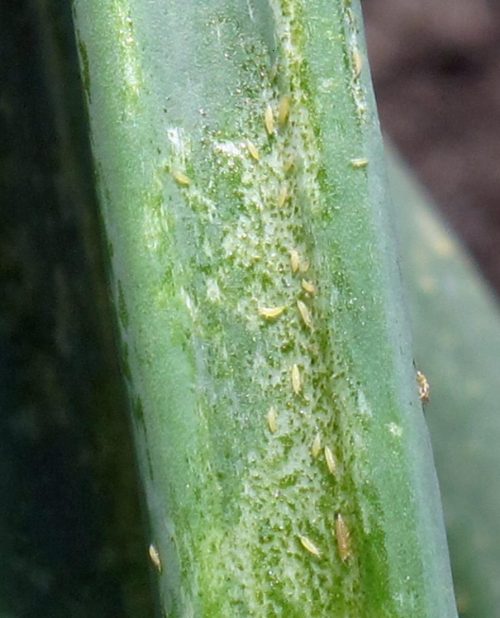
Thrips
They are small insects, hardly visible to the naked eye, that attack a very large number of crop plants. They colonize the tops, flowers, and leaves, causing flower abortion and plant dwarfing.
Control measures:
- garlic treatments with specific insecticides.
Stem and bulb nematode (Ditylenchus dipsaci)
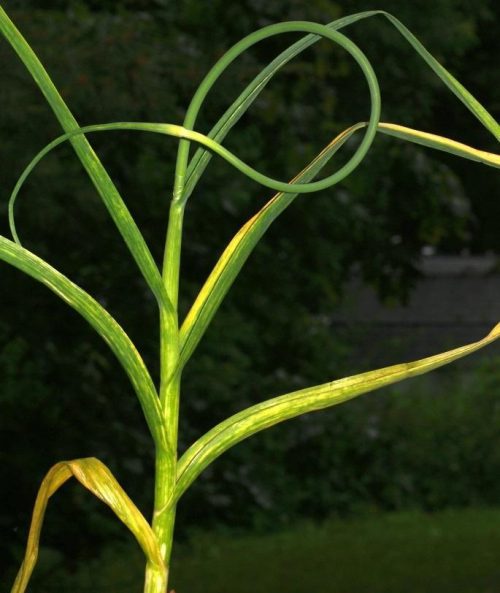
This microscopic pest is present in the soil. Attack on onion and garlic plants can be observed when conditions are optimal (high humidity and temperatures). Symptoms can manifest by leaf twisting and bulb browning. Wounds produced by nematodes are entry points for other pathogens.
Control measures:
- correct crop rotation;
- growing resistant varieties;
- disinfecting soil with specific products.
Leafminer (Liriomyza spp.)
It is a polyphagous species that attacks almost all vegetable species. The larvae produce leaf galls in the form of mining galleries. Adults feed on leaf blades. Other pathogens can settle on wounds caused by this insect.
Control measures:
- garlic treatments with specific insecticides.
Onion fly (Delia antiqua)
This insect also attacks garlic, has two to three generations per year and hibernates as a pupa in the topsoil. The adults emerge in spring and lay their eggs under the soil bulbs near the plants. The larvae burrow into plant tissue, where they dig feeding galleries. Various pathogens settle on the wounds, which can lead to bulb rot.
Control measures:
- collecting plant debris after harvesting;
- carrying out correct autumn plowing;
- treatments during vegetation with specific insecticides.
Wireworms (Agriotes spp.)
This is the larval stage of insects of the genus Agriotes. These larvae attack the root system and bulbs of garlic plants, causing them to deteriorate. Control can be achieved by disinfecting the soil with specific products before planting.